Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Question Answer: Here we are providing Best Solution (Question & Answer) for class 12 Subject Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements. Students can make easily study access all the chapters of Class 12 Chemistry.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Question Answer
Multiple Choice questions-
1. The electrolytic reduction technique is used in the extraction of
(a) Highly electronegative elements.
(b) Highly electropostive elements.
(c) Metalloids.
(d) Transition metals.
2. In the commercial electrochemical process for aluminium extraction, electrolyte used is
(a) Al(OH)3 is NaOH solution.
(b) An aqueous solution of Al2 (SO4)3.
(c) A molten mixture of Al2O3 and Na3AlF6.
(d) A molten mixture of Al2O3 and Al(OH)3.
3. Which ore can be best concentrated by froth floatation process?
(a) Malachite
(b) Cassiterite
(c) Galena
(d) Magnetite
4. Electrolytic reduction of Al2O3 to Al by Hall- Herault process is carried out
(a) in presence of NaCl.
(b) in presence of fluorite.
(c) in presence of cryolite which forms a melt with lower melting point.
(d) in presence of cryolite which forms a melt with high melting point.
5. The chemical composition of ‘slag’ formed during the melting process in the extraction of copper is
(a) Cu2O + FeS
(b) FeSiO3
(c) CuFeS2
(d) Cu2S + FeO
6. Bessemer converter is used in the manufacture of
(a) Pig iron
(b) Steel
(c) Wrought iron
(d) Cast iron
7. The method of zone refining of metals is based on the principle of
(a) greater mobility of the pure metal than that of the impurity.
(b) higher melting point of the impurity than that of the pure metal.
(c) greater noble character of the solid metal than that of impurity.
(d) greater solubility of the impurity in the molten state than in the solid.
8. In the leaching of Ag2S with NaCN, a stream of air is also passed. It is because
(a) The reaction between Ag2S and NaCN is reversible.
(b) to oxidise Na2S formed in the reaction to Na2SO4.
(c) to oxidise Ag2S to Ag2O.
(d) Both (a) and (b).
9. Purest form of iron is
(a) Cast iron
(b) Hard Steel
(c) Stainless steel
(d) Wrought iron
10. Consider the following reaction at 1000° C

Choose the correct statement at 1000°C
(a) Zinc can be oxidised by carbon monoxide.
(b) Zinc oxide can be reduced by graphite.
(c) Both statements (a) and (b) are correct.
(d) Both statements (a) and (b) are false.
Very Short Questions-
1. What is pig iron?
2. What is cast iron?
3. What is wrought iron?
4. What is added as flux in extraction of iron?
5. What is Blister copper?
6. Write the equation for reduction of zinc oxide?
7. Why is cryolite used during extraction of Aluminium?
8. How is copper extracted from low grade ores?
9. State one limitation of Ellingham diagrams.
10. Give an example of extraction based on oxidation reduction.
Short Questions-
1. Sulphide and carbonate ores are converted to oxide before reduction. Why?
2. What is calcinations and roasting? Give one example of each?
3. What is slag? Give an example.
4. How does a reducing agent helps in reduction?
5. Write the relationship between Gibbs free energy, enthalpy change and change in entropy?
6. What is the condition for a reduction reaction to occur in terms of free energy change? How can it be achieved?
7. What are Ellingham diagrams?
8. Give the requirements for vapour phase refining?
9. What is the basis of reduction of a molten metal salt? Explain
10. Which of the ores mentioned in Table 6.1 can be concentrated by magnetic separation method?
Long Questions-
1. What is the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium?
2. Explain: (i) Zone refining (ii) Column chromatography.
3. Write down the reactions taking place in different zones in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron.
4. Write chemical reactions taking place in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende.
5. How can you separate alumina from silica in bauxite ore associated with silica? Give equations, if any.
6. Giving examples, differentiate between ‘roasting’ and ‘calcination’.
7. The choice of a reducing agent in a particular case depends on thermodynamic factor. How far do you agree with this statement? Support your opinion with two examples.
8. Name the processes from which chlorine is obtained as a by-product. What will happen if an aqueous solution of NaCl is subjected to electrolysis?
Assertion and Reason Questions:
1. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Coke and flux are used in smelting.
Reason: The phenomenon in which ore is mixed with suitable flux and coke is heated to fusion is known as smelting.
2. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Leaching is a process of reduction.
Reason: Leaching involves treatment of the ore with a suitable reagent so as to make it soluble while impurities remains insoluble.
MCQ Answers-
- Answer: b
- Answer: c
- Answer: c
- Answer: c
- Answer: b
- Answer: b
- Answer: d
- Answer: d
- Answer: d
- Answer: b
Very Short Answers-
- Ans. The iron which is obtained from blast furnace and contains about 4% carbon and many other impurities in smaller amounts like S, P, Si, Mn etc, is called pig iron.
- Ans. Iron obtained by melting pig iron with scrap iron and coke using hot air blast is cast iron.
- Ans. Wrought iron and malleable iron is the purest form of commercial iron which is prepared from cast iron by oxidizing impurities in a reverberatory furnace lined with hematite.
- Ans. Limestone is used as flux in extraction of iron.
- Ans. The solidified copper obtained after extraction has blistered appearance due to evolution of SO2 is called blister copper.
- Ans. The reduction of zinc-oxide is done using coke.

- Ans. Cryolite is used to lower the melting point of alumina and increase conductivity.
- Ans. Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgy from low grade ores. It is leached out using acid or bacteria.
- Ans. Ellingham diagrams only tell us about the feasibility of a reaction. They do not tell anything about the reaction kinetics.
- Ans. An example based on extraction by oxidation is extraction of chlorine from brine.
Short Answers-
Ans 1. Since the reduction of oxide ores involves a decrease in Gibb’s free energy making
Ans 2. Calcination: – It is the process of heating carbonate ore in the absence of air when volatile matter escape leaving behind metal oxide. e.g.


Roasting: – Here ore is heated in a regular supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of metal e.g.


Ans 3. Slag is the substance obtained after flux reacts with impurity.
Flux + Impurity
For example silica is added as flux to remove iron oxide during extraction of copper as ferrous silicate.

Impurity flux
Ans 4. During the reduction of the metal oxide, the reducing agent combines with oxygen of metal oxide and gets itself oxidized.

Here carbon is reducing agent.
Ans 5. When ΔS is entropy change, ΔH is enthalpy change, then at temperature T, the change in Gibbs free energy is given by
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS.
Ans 6. When the value of ΔG is negative, the reduction reaction is said to be spontaneous
1) If
2) For a process which is otherwise having ΔG positive & is non- spontaneous, it can be coupled with a reaction having highly negative ΔG value so that the overall ΔG is negative and the process can take place.
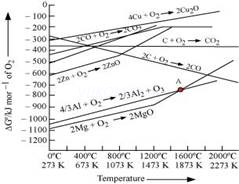
Ans 7. Ellingham diagrams are graphical representation of variation of ΔG vs T for the formation of oxides of elements i.e., for the reaction

Ans 8. The two requirements of vapour phase refining are: –
1) The metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent,
2) The volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that recovery is easy.
Ans 9. In the reduction of molten metal salt, electrolysis is done which is based on electrochemical principles following equation ΔG = -nFE0
Here n is the number of electrons and E0 is the electrode potential of redox couple. More reactive metals have large negative values of the electrode potential and are difficult to reduce.
Ans 10. If the ore or the gangue can be attracted by the magnetic field, then the ore can be concentrated by the process of magnetic separation. Among the ores mentioned in table 6.1, the ores of iron such as haematite Fe2O3 , magnetite (Fe2O4 ), siderite (FeO3) and iron pyrites (Fe2S3)can be separated by the process of magnetic separation.
Long Answers-
Ans 1. In the extraction of aluminium, the significance of leaching is to concentrate pure alumina (Al2O3)from bauxite ore.
Bauxite usually contains silica, iron oxide, and titanium oxide as impurities. In the process of leaching, alumina is concentrated by digesting the powdered ore with a concentrated solution of NaOH at 473-523 K and 35-36 bar. Under these conditions, alumina (Al2O3)dissolves as sodium meta-aluminate and silica (SiO2) dissolves as sodium silicate leaving the impurities behind.

Alumina

The impurities are then filtered, and the solution is neutralized by passing CO2 gas. In this process, hydrated (Al2O3) gets precipitated and sodium silicate remains in the solution. Precipitation is induced by seeding the solution with freshly prepared samples of hydrated (Al2O3).

Hydrated alumina thus obtained is filtered, dried, and heated to give back pure alumina (Al2O3).

Ans 2. (i)

This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the rod also moves with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass onto the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times, which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. Then, the end with the impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, gallium, indium etc. can be purified by this process.
(ii) Column chromatography:

Column chromatography is a technique used to separate different components of a mixture. It is a very useful technique used for the purification of elements available in minute quantities. It is also used to remove the impurities that are not very different in chemical properties from the element to be purified. Chromatography is based on the principle that different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent. In chromatography, there are two phases: mobile phase and stationary phase. The stationary phase is immobile and immiscible. Al2O3 column is usually used as the stationary phase in column chromatography. The mobile phase may be a gas, liquid, or supercritical fluid in which the sample extract is dissolved. Then, the mobile phase is forced to move through the stationary phase. The component that is more strongly adsorbed on the column takes a longer time to travel through it than the component that is weakly adsorbed. The adsorbed components are then removed (eluted) using a suitable solvent (eluant).
Ans 3.

During the extraction of iron, the reduction of iron oxides takes place in the blast furnace. In this process, hot air is blown from the bottom of the furnace and coke is burnt to raise the temperature up to 2200 K in the lower portion itself. The temperature is lower in the upper part. Thus, it is the lower part where the reduction of iron oxides (Fe2O3 and Fe3O4) takes place.
The reactions taking place in the lower temperature range (500 – 800 K) in the blast furnace are:



The reaction taking place in the higher temperature range (900 – 1500 K) in the blast furnace are:


The silicate impurities of the ore is removed as slag by calcium oxide (CaO), which is formed by the decomposition of limestone (CaCO3).


Ans 4. The different steps involved in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende (ZnS) are given below:
(i) Concentration of ore
First, the gangue from zinc blende is removed by the froth floatation method.
(ii) Conversion to oxide (Roasting)
Sulphide ore is converted into oxide by the process of roasting. In this process, ZnS is heated in a regular supply of air in a furnace at a temperature, which is below the melting point of Zn.

(iii) Extraction of zinc from zinc oxide (Reduction)
Zinc is extracted from zinc oxide by the process of reduction. The reduction of zinc oxide is carried out by mixing it with powdered coke and then, heating it at 673 K.

(iv) Electrolytic Refining
Zinc can be refined by the process of electrolytic refining. In this process, impure zinc is made the anode while a pure copper strip is made the cathode. The electrolyte used is an acidified solution of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4). Electrolysis results in the transfer of zinc in pure from the anode to the cathode.
Anode:

Cathode:
Ans 5. To separate alumina from silica in bauxite ore associated with silica, first the powdered ore is digested with a concentrated NaOH solution at 473 – 523 K and 35 – 36 bar pressure. This results in the leaching out of alumina (Al2O3) as sodium aluminate and silica (SiO2) as sodium silicate leaving the impurities behind.


Then, CO2 gas is passed through the resulting solution to neutralize the aluminate in the solution, which results in the precipitation of hydrated alumina. To induce precipitation, the solution is seeded with freshly prepared samples of hydrated alumina.

During this process, sodium silicate remains in the solution. The obtained hydrated alumina is filtered, dried, and heated to get back pure alumina.

Ans 6. Roasting is the process of converting sulphide ores to oxides by heating the ores in a regular supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. For example, sulphide ores of Zn, Pb, and Cu are converted to their respective oxides by this process.



On the other hand, calcination is the process of converting hydroxide and carbonate ores to oxides by heating the ores either in the absence or in a limited supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. This process causes the escaping of volatile matter leaving behind the metal oxide. For example, hydroxide of Fe, carbonates of Zn, Ca, Mg are converted to their respective oxides by this process.



Ans 7.



Assertion and Reason Answers:
1. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Non fusible mass present in ore in mixing with suitable flux are fused which are then reduced by coke to give free metal.
2. (d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Explanation:
Leaching is a process of concentration.
Class 12 Chemistry All Chapter Notes & Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Question Answer

