Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Question Answer: Here we are providing Best Solution (Question & Answer) for class 12 Subject Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry. Students can make easily study access all the chapters of Class 12 Chemistry.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Question Answer
Multiple Choice questions-
Question 1.Movement of dispersion medium under the influence of electric field is known as
(a) electrodialysis
(b) electrophoresis
(c) electroosmosis
(d) cataphoresis.
Question 2. At CMC (Critical Micellisation Cone.) the surface molecules
(a) associate
(b) dissociate
(c) decompose
(d) become completely soluble.
Question 3. Milk is an example of
(a) emulsion
(b) suspension
(c) foam
(d) sol.
Question 4. Tyndall effect is due to
(a) electric charge
(b) scattering of light
(c) absorption of light
(d) none of these.
Question 5. Fog is a colloidal system of
(a) liquid dispersed in a gas
(b) gas dispersed in a gas
(c) solid dispersed in gas
(d) solid dispersed in liquid
Question 6. Blood may be purified by
(a) coagulation
(b) dialysis
(c) electro-osmosis
(d) filtration
Question 7. Blue colour of water in sea is due to
(a) refraction of blue light by impurities in sea water
(b) scattering of light by water
(c) refraction of blue sky by water
(d) None of these
Question 8.The cause of Brownian movement is
(a) heat change in liquid state
(b) attractive force between colloidal particles and dispersion medium
(c) bombardment of the colloidal particles by the molecules of the dispersion medium
(d) interaction of charged particles
Question 9.Emulsifying agent present in milk that makes it stable is
(a) maltose
(b) casein
(c) lactose
(d) none of these
Question 10. Cloud is an example of
(a) liquid dispersed in gas
(b) solid dispersed in gas
(c) solid dispersed in liquid
(d) none of these
Very Short Question:
Question 1. What do you mean by the term –Adsorption?
Question 2. Explain the terms – Adsorbate and Adsorbent with examples
Question 3. Why do finely divided solids act as good adsorbents?
Question 4. What is the sign of ΔH, ΔS and ΔG when a gas is adsorbed by an adsorbent and when ΔG becomes zero?
Question 5. Name the factors which influence the extent of adsorption of a gas on solid.
Question 6. What is adsorption isotherm?
Question 7. for chemisorption is high. why?
Question 8. Give an equation showing variation of extent of adsorption with concentration of a solution?
Question 9. What are positive and negative catalysts? Explain.
Question 10. What do you mean by the term promoter? Give an example.
Short Questions:
Question 1. Explain modern theory of heterogeneous catalysis:
Question 2. Differentiate between lyophobic and lyophilic sol?
Question 3. Distinguish between the meaning of the term’s adsorption and absorption.
Give one example of each.
Question 4. Why is adsorption always exothermic?
Question 5. How are colloids classified on the basis of
- Physical states of components
- Nature of dispersion medium and
- Interaction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium?
Question 6. Explain what is observed:
- When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol.
- An electrolyte, NaCl is added to hydrated ferric oxide sol.
- Electric current is passed through a colloidal sol?
Question 7. Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Comment.
Question 8. What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts?
Question 9. Explain the terms with suitable examples: (i) Alcosol (ii) Aerosol (iii) Hydrosol
Long Questions:
Question 1. Explain Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Question 2.What are homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis? Give example.
Question 3. Explain the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
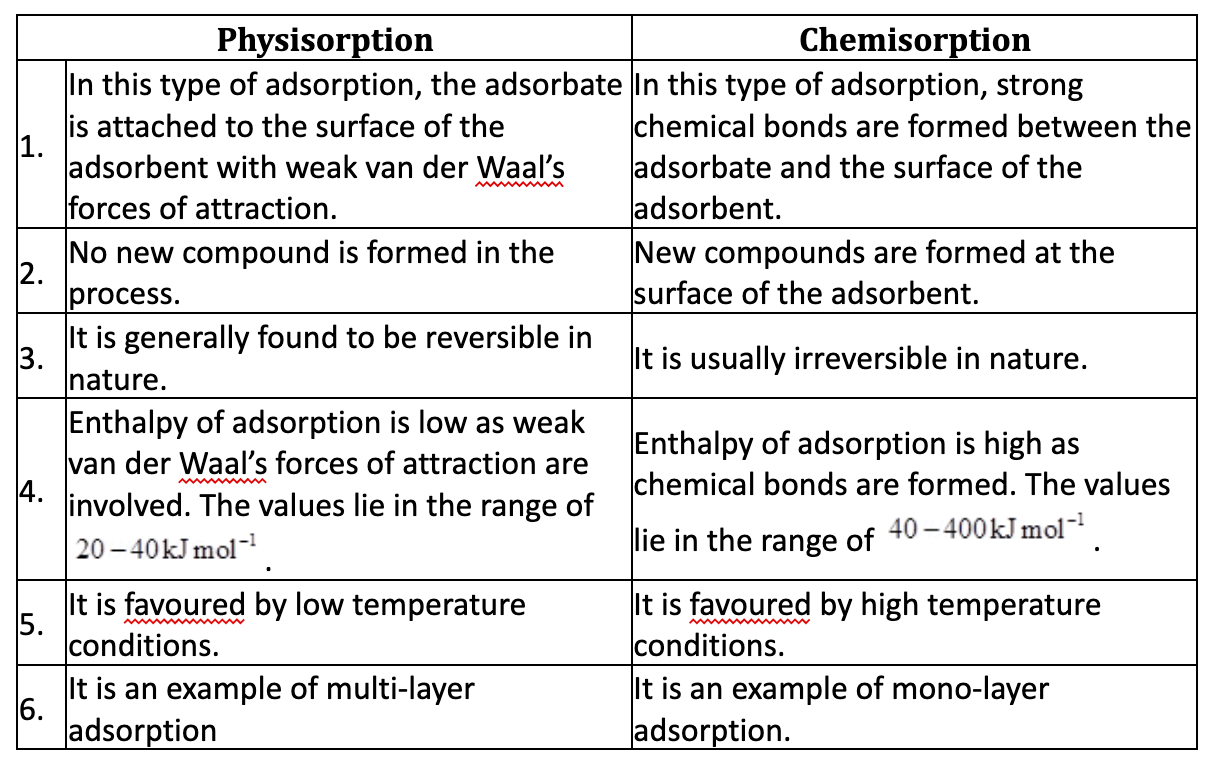
Question 4. What is the difference between physisorption and chemisorption?
Question 5. What are the factors which influence the adsorption of a gas on a solid?
Assertion and Reason Questions:
1. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Porous or finely divided fonns of adsorbents adsorb larger quantities of adsorbate.
Reason: The greater the specific area of the solid, the greater would be its adsorbing capacity.
2. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Aqueous gold colloidal solution is red in colour.
Reason: The colour arises due to scattering of tight by colloidal gold particles.
Case Study Questions:
1. Adsorption is a spontaneous process and involves unequal distribution of the molecules of the gaseous substance on the surface of solid or liquid. Adsorption is an exothermic process. The attractive forces between adsorbate and adsorbent are either van der Waals’ forces or chemical bonds. Adsorption of gases on solids is generally controlled by the factors like temperature, pressure and nature of adsorbate and adsorbent.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
- ln physisorption process, the attractive forces between adsorbate and adsorbent are:
- Covalent bonds.
- Ionic bonds.
- Van der Waals’ forces.
- H-bonds.
- Which of the following graph represents the variation of physical adsorption with temperature?

- Which one of the following processes does not use adsorption?
- Froth floatation process.
- Chromatography.
- Decolourisation of sugar liquors.
- Dissolution of sugar in water.
- Which of the following statements is true?
- Chemisorption forms unimolecular layer.
- Chemisorption is a reversible process.
- Chemisorption is independent of pressure.
- Chemisorption has low enthalpy change.
- Methylene blue, from its aqueous solution, is adsorbed on activated charcoal at 25ºC. For this process, the correct statement is:
- The adsorption requires activation at 25ºC.
- The adsorption is accompanied by a decrease in enthalpy.
- The adsorption increases with increase of temperature
- The adsorption is irreversible.
2. Adsorption depends on the nature of the adsorbent. The rough solid surface has more number of pores and adsorb more number of gases than the smooth surface. Most common adsorbents are silica gel, activated charcoal. The extent of adsorption also depends on the surface area of the solid. Specific surface area of an adsorbent is the surface area available for adsorption per gram of the adsorbent. The greater the surface area of the solid, the greater would be the adsorption. Charcoal is a more effective adsorbent than solid wood. Desorption is a process of removing an adsorbed substance from a surface on which it is absorbed.
Physisorpti on is non-specific and any gas can be adsorbed. But the gases which are easily liquefiable (e.g., NH3, HCl, CO2) are adsorbed at a faster rate and to a large extent than the gases which are difficult to liquefy (e.g., H2, O2, N2). It depends on the critical temperature. Higher the critical temperature of a gas, more easily liquefiable the gas is and more is the rate of adsorption. Chemisorption is specific in nature. Therefore, only those gases can be adsorbed which are capable of forming chemical bonds with the adsorbent.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
- Select the correct statement regarding desorption.
- It is done by cooling or by increasing the pressure applied.
- It is done by cooling or by reducing the pressure applied.
- It is done by heating or by reducing the pressure applied.
- It is done by heating or by increasing the pressure applied.
- Which of the following statements regarding the physical adsorption of a gas on surface of solid is not correct?
- On increasing temperature, adsorption increases continuously.
- Enthalpy changes are negative.
- It is non-specific in nature.
- It is reversible in nature.
- At the same temperature and pressure, select the correct order of adsorption of the following gases on the same mass of charcoal.
- SO2 > CH4 > H2
- CH4 < SO2 < H2
- H2 > CH4 > SO2
- CH4 < H2 < SO2
- Select the correct option among the following when adsorption of a gas on solid metal surface is spontaneous and exothermic.
- △S increases
- △S decreases
- △G increases
- △H increases
- Select the incorrect statement among the following.
- Physical adsorption occurs at a low temperature and chemisorption occurs at all temperature.
- ln physisorption heat of adsorption is low while in chemisorption it is high.
- Chemisorption is irreversible and physisorption is reversible.
- Magnitude of chemisorption decreases with rise in temperature while physisorption increases with rise in temperature.
Answers key
MCQ answers:
- Answer: (c) electroosmosis
- Answer: (a) associate
- Answer (a) emulsion
- Answer: (b) scattering of light
- Answer: (a) liquid dispersed in a gas
- Answer: (b) dialysis
- Answer: (a) refraction of blue light by impurities in sea water
- Answer: (c) bombardment of the colloidal particles by the molecules of the dispersion medium
- Answer: (b) casein
- Answer: (a) liquid dispersed in gas
Very Short Answers:
- The accumulation of molecular species at the surface rather than in bulk of a solid liquid is termed as Adsorption
- The molecular species which get concentrated or accumulated at the surface are adsorbate eg. O2, H2, CO, Cl2, NH3etc. and the material on the surface of which the adsorption takes place is adsorbent. eg. Charcoal, silica gel, alumina gel, clay etc
- Answer: Powdering of solids increase its surface and therefore it can adsorb a greater amount of the adsorbate. Thus, finely divided solids act as good adsorbents.
- Answer:
is negative,
is negative and
is negative. When
=
the
is zero. This state equilibrium is attained.
- Answer: Factors affecting extent of adsorption are –
(i) Nature of adsorbent and adsorbate.
(ii) Surface area of solid
(iii) Pressure of gas
(iv) Temperature.
- Answer: The variation in the amount of gas adsorbed by the adsorbent with pressure at constant temperature can be expressed by means of a curve known as adsorption isotherm.
- Answer: In chemisorption, chemical bonds are formed that evolves a large amount of energy. Therefore for chemisorption is high.
- x/m = KC1/n (n>1) Where x/m is the extent of adsorption – k &n are constants and c is the concentration of solution.
- . A catalyst which increases the rate of a reaction is positive catalyst and which decrease the rate is a negative catalyst.
- Promoters are substances that enhance the activity of a catalyst e.g. molybdenum acts as a promoter in Haber’s process.
Short Answers:
- Answer According to modern theory of catalysis, the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysis involves following steps –
- Diffusion of reactants on the surface of catalyst.
- Adsorption of reactant molecules on the surface.
- Occurrence of reaction on the catalysts surface through formation of an intermediate.
- Desorption of products from surface.
- Diffusion of products away from surface.
- Answer:
| Lyophobic sol | Lyophilic sol. |
| 1. It is relatively unstable due to Repulsion between dispersion medium and dispersed phase. | 1. It is relatively more stable due to med- attraction between dispersion medium and dispersed Phase. |
| 2. It is irreversible. | 2. It is reversible. |
| 3. It cannot be easily peptised. | 3. It can be easily peptised. |
| 4. Small quantities of electrolyte cause precipitation. | 4. Small quantities of electrolyte has no effect larger concentration causes precipitation. |
- Answer: Adsorption is a surface phenomenon of accumulation of molecules of a substance at the surface rather than in the bulk of a solid or liquid. The substance that gets adsorbed is called the ‘adsorbate’ and the substance on whose surface the adsorption takes place is called the ‘adsorbent’. Here, the concentration of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent increases. In adsorption, the substance gets concentrated at the surface only. It does not penetrate through the surface to the bulk of the solid or liquid. For example, when we dip a chalk stick into an ink solution, only its surface becomes coloured. If we break the chalk stick, it will be found to be white from inside.On the other hand, the process of absorption is a bulk phenomenon. In absorption, the substance gets uniformly distributed throughout the bulk of the solid or liquid.
- Answer:Ans. Adsorption is always exothermic. This statement can be explained in two ways.
(i) Adsorption leads to a decrease in the residual forces on the surface of the adsorbent. This causes a decrease in the surface energy of the adsorbent. Therefore, adsorption is always exothermic.
(ii) ΔH of adsorption is always negative. When a gas is adsorbed on a solid surface, its movement is restricted leading to a decrease in the entropy of the gas i.e.,
Therefore,ΔG = ΔH-TΔS
Since ΔS is negative, ΔH has to be negative to make ΔG negative. Hence, adsorption is always exothermic.
5. Answer :
Colloids can be classified on various bases:
(i) On the basis of the physical state of the components (by components we mean the dispersed phase and dispersion medium). Depending on whether the components are solids, liquids, or gases, we can have eight types of colloids.
(ii) On the basis of the dispersion medium, sols can be divided as:
| Dispersion medium | Name of sol |
| Water | Aquasol or hydrosol |
| Alcohol | Alcosol |
| Benzene | Benzosol |
| Gases | Aerosol |
(iii) On the basis of the nature of the interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium, the colloids can be classified as lyophilic (solvent attracting) and lyophobic (solvent repelling).
- Answer:
i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution, then scattering of light is observed. This is known as the Tyndall effect. This scattering of light illuminates the path of the beam in the colloidal solution.
(ii) When NaCl is added to ferric oxide sol, it dissociates to give and ¬ ions. Particles of ferric oxide sol are positively charged. Thus, they get coagulated in the presence of negatively charged ions.
(iii) The colloidal particles are charged and carry either a positive or negative charge. The dispersion medium carries an equal and opposite charge. This makes the whole system neutral. Under the influence of an electric current, the colloidal particles move towards the oppositely charged electrode. When they come in contact with the electrode, they lose their charge and coagulate.
7. Answer:
The cleansing action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Soaps are basically sodium and potassium salts of long chain fatty acids, . The end of the molecule to which the sodium is attached is polar in nature, while the alkyl-end is non-polar. Thus, a soap molecule contains a hydrophilic (polar) and a hydrophobic (non-polar) part.
When soap is added to water containing dirt, the soap molecules surround the dirt particles in such a manner that their hydrophobic parts get attached to the dirt molecule and the hydrophilic parts point away from the dirt molecule. This is known as micelle formation. Thus, we can say that the polar group dissolves in water while the non-polar group dissolves in the dirt particle. Now, as these micelles are negatively charged, they do not coalesce, and a stable emulsion is formed.
8. Answer:
The activity of a catalyst is its ability to increase the rate of a particular reaction. Chemisorption is the main factor in deciding the activity of a catalyst. The adsorption of reactants on the catalyst surface should be neither too strong nor too weak. It should just be strong enough to make the catalyst active.
(b) Selectivity of the catalyst:
The ability of the catalyst to direct a reaction to yield a particular product is referred to as the selectivity of the catalyst. For example, by using different catalysts, we can get different products for the reaction between H2 and CO.

9. Answer :
A colloidal solution having alcohol as the dispersion medium and a solid substance as the dispersed phase is called an alcosol.
For example: colloidal sol of cellulose nitrate in ethyl alcohol is an alcosol.
(ii) Aerosol:
A colloidal solution having a gas as the dispersion medium and a solid as the dispersed phase is called an aerosol.
For example: fog
(iii) Hydrosol
A colloidal solution having water as the dispersion medium and a solid as the dispersed phase is called a hydrosol. For example: starch sol or gold sol.
Long Answers:
- Answer:


2. Answer:
When reactant and catalyst are in the same phase, the process is said to be homogeneous catalysis.
Examples –
(1) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide in the presence of oxygen gas and nitric oxide gas as catalyst.

(2) Hydrolysis of methyl acetate catalysed by H+ ions.

(3) Hydrolysis of sugar catalysed by H2SO4.
Heterogeneous Catalysis –
The catalytic process in which the reactant and catalyst are in different phases is known as heterogeneous catalysis.
Examples: –
(1) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide in presence of platinum

(2) Preparation of ammonia by Haber’s process

(3) Oxidation of ammonia in Ostwald’s process.

- Answer
Mechanism of enzyme catalysed reactions-
There are active centres or cavities on the surface of enzyme particles. The molecules of the reaction or substrate which have complementary shape fit into these just like a key fit into a lock. This forms an activated complex which decomposes to yield products. The reactions proceed in two steps –
Step 1: Binding of enzymes to substrate to form activated complex.
Step 2: Decomposition of complex to form products.


- Answer:

- Answer:
There are various factors that affect the rate of adsorption of a gas on a solid surface.
(1) Nature of the gas: Easily liquefiable gases such as
(2) Surface area of the solid :The greater the surface area of the adsorbent, the greater is the adsorption of a gas on the solid surface.
(3) Effect of pressure :Adsorption is a reversible process and is accompanied by a decrease in pressure. Therefore, adsorption increases with an increase in pressure.
(4) Effect of temperature :Adsorption is an exothermic process. Thus, in accordance with Le-Chatelier’s principle, the magnitude of adsorption decreases with an increase in temperature.
Assertion and Reason Answers:
1. (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Explanation:
Porous or finely divided fonns of adsorbent possess greater specific area which is available for adsorption per gram of the adsorbent.
2. (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Explanation:
The colour of colloidal solution depends on the wavelength of light scattered by the dispersed particles. The wavelength of light further depends on the size and nature of the particles. Finest gold sol is red in colour. As size of the particles increases, it becomes purple, then blue and finally golden yellow.
Case Study Answers:
Answer :
- (c) Van der Waals’ forces.
Explanation:
ln physisorption process, the attractive forces between adsorbate and adsorbent are van der Waals’ forces.

- (d) Dissolution of sugar in water.
- (a) Chemisorption forms unimolecular layer.
- (b) The adsorption is accompanied by a decrease in enthalpy.
Explanation:
The adsorption of methylene blue on activated charcoal is physical adsorption. lt is accompanied by a decrease in enthalpy.
2. Answer :
- (c) It is done by heating or by reducing the pressure applied.
Explanation:
Desorption is done by heating or by reducing the pressure applied.
- (a) On increasing temperature, adsorption increases continuously.
Explanation:
Physisorption is exothermic in nature. Therefore, according to Le Chatelier’s principle, it occurs readily at low temperature and decreases with increase in temperature. Bonds between surface and adsorbate are weak so when temperature is increased the bonds break easily, so rate will decrease on increasing temperature.
- (a) SO2 > CH4 > H2
Explanation:
Higher the critical temperature of a gas, greater is the amount of gas adsorbed. Critical temperature (in Kelvin) of the gases:
H2 < CH4 < SO2
33.2 190.6 430.3
- (b) △S decreases
Explanation:
Since for spontaneous and exothermic process,
△G = −ve, △H = −ve at all temperatures, therefore from △G = △H −T△S, △S should be -ve. Also adsorption of gas on solid surface gives more orderly arrangement.
- (d) △H increases
Explanation:
Chemisorption first increases with increase of temperature. Physisorption decreases with rise in temperature.
Class 12 Chemistry All Chapter Notes & Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Question Answer