Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Question Answer: Here we are providing Best Solution (Question & Answer) for class 12 Subject Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics. Students can make easily study access all the chapters of Class 12 Chemistry.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Question Answer
Multiple Choice questions-
Question 1.A first order reaction has a half life period of 34.65 seconds. Its rate constant is
(a) 2 × 10-2 s-1
(b) 4 × 10-4 s-1
(c) 20 s-1
(d) 2 × 10-4 s-1
Question 2.If a graph is plotted between In k and 1/T for the first order reaction, the slope of the straight line so obtained is given by
Question 3.The unit of rate constant for a zero order reaction is
(a) mol L-1s-1
(b) s-1
(c) L mol-1s-1
(d) L2mol-2s-1
Question 4.A catalyst increases the speed of a chemical reaction by
(a) increasing activation energy
(b) decreasing activation energy
(c) increasing reactant energy
(d) decreasing threshold energy
Question 5.The units of the rate constant for the second order reaction are:
(a) mol-1 litre s-1
(b) mol litre-2 s-1
(c) s-1
(d) mol litre-1 s-1
Question 6.The value of k for a reaction is 2.96 × 10-30 s-1. What is the order of the reaction?
(a) Zero
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1
Question 7.A reaction is found to be of second order with respect to concentration of carbon monoxide. If concentration of carbon monoxide is doubled, the rate of reaction will
(a) triple
(b) increase by a factor of 4
(c) double
(d) remain unchanged
Question 8. If the concentrations are expressed in mol litre-1 and time in s, then the units of rate constant for the first-order reactions are
(a) mol litre-1 s-1
(b) mol-1 litre s-1
(c) s-1
(d) mol² litre-2 s-1
Question 9.The half life of a first order reaction having rate constant 200 s-1 is
(a) 3.465 × 10-2 s
(b) 3.465 × 10-3 s
(c) 1.150 × 10-2 S
(d) 1.150 × 10-3 S
Question 10.The rate of a reaction is 1.209 × 10-4L² mol-2s-1. The order of the reaction is:
(a) zero
(b) first
(c) second
(d) third
Very Short Question:
Question 1. Is rate of reaction always constant?
Question 2. Can order of reaction be zero? Give example.
Question 3. What do you understand by rate law expression?
Question 4. Is it possible to determine or predict the rate law theoretically by merely looking at the equation?
Question 5. Define the term chemical kinetics?
Question 6. Define – Rate of reaction and the factors affecting the rate of reaction.
Question 7. What is average rate of a reaction? How is it determined?
Question 8. What are the units of rate of a reaction?
Question 9. Identify the reaction order for from each of the following rate constant –
(a)
(b)
Question 10. Consider the equation

The rate law for this equation is first order with respect to
Short Questions:
Question 1 For the reaction A+
B
Question 2. . A chemical reaction 2A
Question 3. For the following reactions, write the rate of reaction expression in terms of reactants and products?

Determine
i) The order
ii) The rate law.
iii) Rate constant for the reaction.
Question 5. The following experimental data was collected for the reaction:

Construct the rate equation for the reaction.
Question 6. Draw a graph for
a) Concentration of reactant against time for a zero order reaction.
b) Log Ro/ R against time for a first order reaction.
Question 7. In general it is observed that the rate of a chemical reaction doubles with every


Question 9. Plot a graph showing variation of potential energy with reaction. coordinate?
Question 10. The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
Long Questions:

Question 3. From the rate expression for the following reactions, determine their order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constants.

Question 4. The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of N2 and H2 if k= 2.5 X 10-4 mol-1L s-1?
Question 5. The decomposition of dimethyl ether leads to the formation of CH4, H2,and CO and the reaction rate is given by Rate = K[CH3OCH3]3/2. The rate of reaction is followed by increase in pressure in a closed vessel, so the rate can also be expressed in terms of the partial pressure of dimethyl ether, i.e., Rate = k(PCH3OCH3)3/2If the pressure is measured in bar and time in minutes, then what are the units of rate and rate constants?
Assertion and Reason Questions:
1. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: The rate ofreaction is always negative.
Reason: Minus sign used in expressing the rate shows that concentration of product is decreasing.
2. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertionss.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Kinetics explains the reaction mechanism.
Reason: Kinetics explains the formation of products.
Case Study Questions:
1. ln a reaction, the rates of disappearance of different reactants or rates of formation of different products may not be equal but rate of reaction at any instant of time has the same value expressed in terms of any reactant or product. Further, the rate of reaction may not depend upon the stoichiometric coefficients of the balanced chemical equation. The exact powers of molar concentrations of reactants on which rate depends are found experimentally and expressed in terms of ‘order of reaction’. Each reaction has a characteristic rate constant depends upon temperature. The units of the rate constant depend upon the order of reaction.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
- The rate constant of a reaction is found to be 3 × 10-3 mol-2 L2 sec-1. The order of the reaction is:
- 0.5
- 2
- 3
- 1
- ln the reaction, A + 3B → 2C, the rate of formation of C is:
- The same as rate of consumption of A.
- The same as the rate of consumption of B.
- Twice the rate of consumption of A.
- 3232 times the rate of consumption of B.
- Rate of a reaction can be expressed by following rate expression, Rate = k[A]2 [B], if concentration of A is increased by 3 times and concentration of B is increased by 2 times, how many times rate of reaction increases?
- 9 times
- 27 times
- 18 times
- 8 times
- The rate of a certain reaction is given by, rate = k[H+]n.The rate increases 100 times when the pH changes from 3 to 1. The order (n) of the reaction is:
- 2
- 0
- 1
- 1.5
- ln a chemical reaction A + 2B → products, when concentration of A is doubled, rate of the reaction increases 4 times and when concentration of B alone is doubled rate continues to be the same. The order of the reaction is:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2. The progress of the reaction, A ⇌ nB with time is represented in the following figure:

The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
- What is the value of n?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Find the value of the equilibrium constant.
- 0.6M
- 1.2M
- 0.3M
- 2.4M
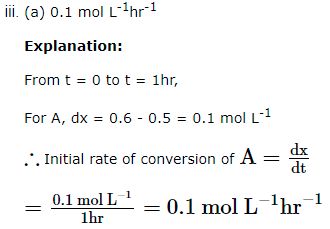
- The initial rate of conversion of A will be:
- 0.1 mol L-1hr-1
- 0.2 mol L-1hr-1
- 0.4 mol L-1hr-1
- 0.8 mol L-1hr-1
- For the reaction, if d[B]dt=210-4, value of d[A]/dt will be:
- 2 × 10-4
- 10-4
- 4 × 10-4
- 0.5 × 10-4
- Which factor has no effect on rate of reaction?
- Temperature.
- Nature of reactant.
- Concentration of reactant.
- Molecularity.
Answers key
MCQ Answer:
- Answer: (a) 2 × 10-2 s-1
- Answer: (a) -Ea/R
- Answer: (a) mol L-1s-1
- Answer: (b) decreasing activation energy
- Answer: (a) mol-1 litre s-1
- Answer: (d) 1
- Answer: (b) increase by a factor of 4
- Answer: (c) s-1
- Answer: (b) 3.465 × 10-3 s
- Answer: (d) third
Very Short Answers:
- No. rate of a reaction is not always constant. It depends on many factors such as concentration, temperature etc.
- Yes, decomposition of ammonia on a hot platinum surface is a zero order of reaction at high pressure
- Answer: The rate law is the expression in which rate is given in terms of molar concentration of reactants with each term raised to some power, which may or may not be same as the stoichiometric coefficient of the reacting species in a balanced chemical equation.
- Answer: No, the rate law cannot be predicted by merely looking at the balanced chemical equation but must be determined experimentally.
- Answer: The branch of chemistry that deals with the study of reaction rates and their mechanisms is called chemical Kinetics.
- Answer: Rate of reaction can be defined as the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time. Factors affecting the rate of reaction are temperature, concentration of reactants and catalyst.
- Answer: Average rate of a reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a reactant or a product per unit time. It can be determined by dividing the change in concentration of reactant or product by the time interval
For the reaction: A

- The units of rate of a reaction are Mol L-1S-1 In gaseous reaction the unit of rate of reaction is atom .
- a) Since the units of rate constant are L mol-1S-1 The reactions is of second order.
b) Since the units of rate constant areS-1, The reaction is of first order - The rate law will be R=K[NO]2[H2]
Short Answers:
- Answer
. A+B
Rate [A]2
Rate = 1 when A = 1 ———- 1)
Rate = 2 when A = 2———–2)
Dividing equation 2) by 1)

The reaction is first order reaction.
- Answer:
2A

- Rate of disappearance of B


- Answer:
Let the order of reaction be x

6. Answer

- Answer:

- Answer :

- Answer :

Long Answers:
- Answer:

2. Answer:

3. Answer:


4. Answer:

- Answer:

Assertion and Reason Answers:
1. (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Explanation:
The rate reaction is never negative. Minus sign used in expressing the rate only shows that the concentration of the reactant is decreasing.
2. (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Explanation:
Kinetics deals with the reaction mechanism i.e., how the atoms rearrange themselves in the reactant molecules in a single step or a number of steps, finally leading to the product molecules.
Case Study Answers:
1. Answer :





2. Answer :




Class 12 Chemistry All Chapter Notes & Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Question Answer

