Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Question Answer: Here we are providing Best Solution (Question & Answer) for class 12 Subject Chemistry 2 Solutions. Students can make easily study access all the chapters of Class 12 Chemistry.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Question Answer
Multiple Choice questions-
Question 1. Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure?
(a) mole fraction
(b) parts per million
(c) mass percentage
(d) molality
Question 2. On dissolving sugar in water at room temperature, solution feels cool to touch. Under which of the following cases dissolution of sugar will be most rapid?
(a) Sugar crystals in cold water.
(b) Sugar crystals in hot water.
(c) Powdered sugar in cold water.
(d) Powdered sugar in hot water.
Question 3. At equilibrium the rate of dissolution of a solid solute in a volatile liquid solvent is
(a) less than the rate of crystallisation
(b) greater than the rate of crystallisation
(c) equal to the rate of crystallisation
(d) zero
Question 4. A beaker contains a solution of substance ‘A’. Precipitation of substance ‘A’ takes place when small amount of ‘A’ is added to the solution. The solution is ………………
(a) saturated
(b) supersaturated
(c) unsaturated
(d) concentrated
Question 5. Maximum amount of a solid solute that can be dissolved in a specified amount of a given liquid solvent does not depend upon .
(a) temperature
(b) nature of solute
(c) pressure
(d) nature of solvent
Question 6. Low concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitude is due to
(a) low temperature
(b) low atmospheric pressure
(c) high atmospheric pressure
(d) both low temperature and high atmospheric pressure
Question 7. Considering the formation, breaking and strength of hydrogen bond, predict which of the following mixtures will show a positive deviation from Raoult’s law?
(a) Methanol and acetone.
(b) Chloroform and acetone.
(c) Nitric acid and water.
(d) Phenol and aniline.
Question 8. Colligative properties depend on
(a) the nature of the solute particles dissolved in solution.
(b) the number of solute particles in solution.
(c) the physical properties of the solute particles dissolved in solution.
(d) the nature of solvent particles.
Question 9.Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point?
(o) 1.0 M NaOH
(b) 1.0 M Na2SO4
(c) 1.0 M NH4NO3
(d) 1.0 M KNO3
Question 10. The unit of ebullioscopic constant is
(a) K kg mol-1 or K (molality)-1
(b) mol kg K-1 or K-1 (molality)
(c) kg mol-1 K-1 or K-1 (molality)-1
(d) K mol kg-1 or K (molality)
Question 11.In comparison to a 0.01 M solution of glucose, the depression in freezing point of a 0.01 M MgCl2 solution is ………..
(a) the same
(b) about twice
(c) about three times
(d) about six times
Question 12.An unripe mango placed in a concentrated salt solution to prepare pickle shrivels because ………..
(a) it gains water due to osmosis.
(b) it loses water due to reverse osmosis.
(c) it gains water due to reverse osmosis.
(d) it loses water due to osmosis.
Question 13. At a given temperature, osmotic pressure of a concentrated solution of a substance
(a) is higher than that of a dilute solution.
(b) is lower than that of a dilute solution.
(c) is same as that of a dilute solution.
(d) cannot be compared with osmotic pressure of dilute solution.
Question 14. Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Two different solutions of sucrose of same molality prepared in different solvents will have the same depression in freezing point.
(b) The osmotic pressure of a solution is given by the equation π = cRT (where c is the molarity of the solution).
(c) Decreasing order of osmotic pressure for 0.01 M aqueous solutions of barium chloride, potassium chloride, acetic acid and sucrose is BaCl2 > KCl > CH3COOH > sucrose.
(d) According to Raoult’s law, the vapour pressure exerted by a volatile component of a solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution.
Question 15.he values of Van’t Hoff factors for KCl, NaCl and K2SO4, respectively, are
(a) 2, 2 and 2
(b) 2, 2 and 3
(c) 1,1 and 2
(d) 1, 1 and 1
Very Short Question:
Question 1. Define the term – solubility?
Question 2. What is the effect of pressure on solubility of a gas?
Question 3. State Henry’s Law.
Question 4. State Raoult’s Law.
Question 5. What are the factors on which vapour pressure depends?
Question 6. The vapour pressure of solvent gets lowered, when a non- volatile solute is added to it. Why?
Question 7. Name two ways by which vapour pressure of a liquid can be lowered.
Question 8. Define solution?
Question 9. Define the following terms:
(a) Molality
(b) Molarity
Question 10. How does change in temperature changes the molarity and molality values?
Short Questions:
Question 1 Find the molality and molarity of a 15% solution of H2SO4 when its density is
- 1.10 glcm3 & molar mass = 98 amu.
Question 2. Calculate the mole fraction of ethanol and water in a sample of rectified spirit which contains 46% ethanol by mass?
Question 3. Calculate the % composition in terms of mass of a solution obtained by mixing 300g of a 25% & 400 g of a 40% solution by mass?
Question 4. One litre of sea water weight 1030g and contains about of dissolved
Question 5. The density of 85% phosphoric acid is. What is the volume of a solution that contains 17g of phosphoric acid?
Question 6. Define the term azeotrope?
Question 7. Obtain a relationship between relative lowering of vapour pressure and mole fraction of solute?
Question 8. Draw the graphs of both deviations from ideal behaviours?
Question 9. A weak electrolyte AB in 5% dissociated in aqueous solution? What is the freezing point of a 0.10 molar aqueous solution of AB? Kf = 1.86 deg/molal?
Question 10. Henry’s law constant for the molality of methane in benzene at 298 K is . Calculate the solubility of methane in benzene at 298 K under 760 mm Hg.
Long Questions:
Question 1.
The vapour pressure of at is 854 mm Hg .A solution of 2.0g sulphur in 100g of has a vapour pressure of 848.9 mm Hg .Calculate the formula of sulphur molecule
Question 2. Calculate the mass percentage of benzene (C6H6) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride.
Question 3. Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride.
Question 4. Calculate the molarity of each of the following solutions: (a) 30 g of . in 4.3 L of solution (b) 30 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4 diluted to 500mL.
Question 5.Calculate (a)molality (b)molarity and (c)mole fraction of KI if the density of 20% (mass/mass) aqueous KI is
Assertion and Reason Questions:
1. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Camphor is used as a solvent in the determination of molecular masses of naphthalene, anthracene, etc.
Reason: Camphor has high molal elevation constant.
2. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Reverse osmosis is used in the desalination of sea water.
Reason: When pressure more than osmotic pressure is applied, pure water is squeezed out of the sea water through the membrane.
Case Study Questions:
1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The solubility of gases increases with increase of pressure. William Henry made a systematic investigation of the solubility of a gas in a liquid. According to Henry’s law “the mass of a gas dissolved per unit volume of the solvent at constant temperature is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas in equilibrium with the solution”. Dalton during the same period also concluded independently that the solubility of a gas in a ti quid solution depends upon the partial pressure of the gas. If we use the mole fraction of gas in the solution as a measure of its solubility, then Henry’s law can be modified as “the partial pressure of the gas in the vapour phase is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the gas in the solution”
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
- Henry’s law constant for the solubility of methane in benzene at 298K is 4.27 x 105mm Hg. The solubility of methane in benzene at 298K under 760mm Hg is:
- 4.27 × 10-5
- 1.78 × 10-3
- 4.27 × 10-3
- 1.78 × 10-5
- The partial pressure of ethane over a saturated solution containing 6.56 × 10-2g of ethane is I bar. If the solution contains 5.00 × 10-2g of ethane then what will be the partial pressure (in bar) of the gas?
- 0.762
- 1.312
- 3.81
- 5.0
- KH (K bar) values for Ar(g), CO2(g), HCHO(g) and CH4(g) are 40.39, 1.67, 1.83 × 10-5 and 0.413 respectively. Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility. Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility.
- HCHO < CH4 < CO2 < Ar
- HCHO < CO2 < CH4 < Ar
- Ar < CO2 < CH4 < HCHO
- Ar < CH4 < CO2 < HCHO
- When a gas is bubbled through water at 298K, a very dilute solution of the gas is obtained. Henry’s law constant for the gas at 298K is 150 kbar. If the gas exerts a partial pressure of 2 bar, the number of millimoles of the gas dissolved in IL of water is:
- 0.55
- 0.87
- 0.37
- 0.66
- Which of the following statements is correct?
- KH increases with increase of temperature.
- KH decreases with increase of temperature.
- KH remains constant with increase of temperature.
- KH first increases then decreases, with increase of temperature.
2. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions
Few colligative properties are:
- Relative lowering of vapour pressure: depends only on molar concentration of solute (mole fraction) and independent of its nature.
- Depression in freezing point: it is proportional to the molal concentration of solution.
- Elevation of boiling point: it is proportional to the molal concentration of solute.
- Osmotic pressure: it is proportional to the molar concentration of solute
A solution of glucose is prepared with 0.052 g at glucose in 80.2 g of water. (KJ = 1.86K kg mol-1 and Kb = 5.2K kg mol-1)
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
- Molality of the given solution is.
- 0.0052m
- 0.0036m
- 0.0006m
- 1.29m
- Boiling point for the solution will be.
- 373.05K
- 373.15K
- 373.02K
- 373.02K
- The depression in freezing point of solution will be.
- 0.0187K
- 0.035K
- 0.082K
- 0.067K
- Mole fraction of glucose in the given solution is.
- 6.28 × 10-5
- 6.28 × 10-4
- 0.00625
- 0.00028
- If same amount of sucrose (C12 H22 O11) is taken instead of glucose, then.
- Elevation in boiling point will be higher.
- Depression in freezing point will be higher.
- Depression in freezing point will be lower.
- Both (a) and (b).
Answers key
MCQ answers:
- Answer: (a) mole fraction
- Answer: (d) Powdered sugar in hot water.
- Answer: (c) equal to the rate of crystallisation
- Answer: (b) supersaturated
- Answer: (c) pressure
- Answer: (b) low atmospheric pressure
- Answer: (a) Methanol and acetone.
- Answer: (b) the number of solute particles in solution.
- Answer: (b) 1.0 M Na2SO4
- Answer: (a) K kg mol-1 or K (molality)-1
- Answer: (c) about three times
- Answer: (d) it loses water due to osmosis.
- Answer: (a) is higher than that of a dilute solution.
- Answer: (a) Two different solutions of sucrose of same molality prepared in different solvents will have the same depression in freezing point.
- Answer: (b) 2, 2 and 3
Very Short Answers:
- The maximum amount of a substance that can be dissolved in a specified amount of solvent is called its solubility.
- The solubility of a gas increases with increases of pressure.
- Answer: Henry’s Law states that at a constant temperature the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas.
- Answer: Raoult’s Law states that for a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction.
- Answer: The factors on which vapour pressure depends are –
1) Temperature of the liquid. 2) Nature of the liquid.
- Answer: When a non-volatile solute is added to a solvent, the surface area for escape of solvent molecules decreases and vapour pressure gets lowered.
- Answer: The two ways by which vapour pressure can be lowered are –
1) By decreasing the temperature.
2) By adding a non- volatile solute.
- Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more than two components..
- (a) Molality is defined as the number of moles of the solute per kilogram of solvent.


(b) Molarity (M) = Number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre of solution.


- As the temperature increases, volume increases and molarity decreases whereas molality does not change with any change in temperature.
Short Answers:
- Answer
Volume = mass/density


Molarity =

=

Molality =


= 1.8 M.
- Answer:
Mass of ethanol = 46g

Mass of water = 100 – 46 = 54g
Mole fraction of ethanol,
=

Mole fraction of water = 1-0.25 = 0.75
Mole fraction of water = 1-0.25 = 0.75
- Answer:
mass of solute in 400g of 40%
=

Total mass of solute = 160+75 = 235g
Total mass of solution = 400+300 = 700g
Mass% of solute =

=

Mass % of solvent = 100 – 33.57 = 66.43%
- Answer:
mass of

ppm of O2in 1030 g sea water =

=

5. Answer :
Ans. 85g phosphoric acid is present in 100g of solution.
17g of phosphoric acid is present in

Volume of 17g of 85% acid =


=
6. Answer
A solution at certain concentration when continues to boil at constant temperature without change in its composition in solution & in vapour phase is called an azeotrope.
7. Answer:
According to Raoult’s Law –




=

Relative lowering of vapour pressure.
8. Answer:
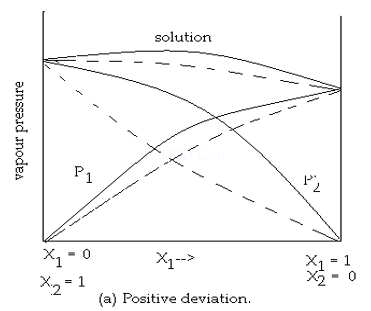

9. Answer :


- Answer :

Long Answers:
- Answer:


2. Answer:

3. Answer:
Let the total mass of the solution be 100 g and the mass of benzene be 30g.
∴ Mass of carbon tetrachloride = (100 – 30) g
= 70 g
Molar mass of benzene (C6H6) = (6 X 12 + 6 X 1) mol g-1
= 78 mol g-1
∴ Number of moles of C6H6= 30/78 mol
= 0.3846 mol
Molar mass of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4 ) = 1×12 + 4 x355
= 154g mol-1
∴Number of moles of

= 0.4545 mol
Thus, the mole fraction of C6H6is given as:


= 0.458
4. Answer:
Molarity is given by:

(a) Molar mass of 59 + 2 (14 + 3

= 291 g mol-1
Therefore, Moles of

= 0.103 mol
Therefore, molarity

= 0.023 M
(b) Number of moles present in 1000 mL of 0.5 M
∴Number of moles present in 30 mL of 0.5 M


= 0.015 mol
Therefore, molarity = 0.03 M

5. Answer:
(a) Molar mass of KI = 39 + 127 = 166 g mol-1
20% (mass/mass) aqueous solution of KI means 20 g of KI is present in 100 g of solution.
That is,
20 g of KI is present in (100 – 20) g of water = 80 g of water
Therefore, molality of the solution=


= 1.506 m
= 1.51 m (approximately)
(b) It is given that the density of the solution =

Therefore, Volume of 100 g solution =

= 83.19 mL
=


Therefore, molarity of the solution =
(c) Moles of KI =

Moles of water =

Therefore, mole fraction of KI =

= 0.0263
Assertion and Reason Answers:
1. (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Explanation:
Camphor has high molal depression constant.
2. (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Explanation:
If a pressure larger than the osmotic pressure is applied to the solution side, the pure solvent flows out of the solution to the solvent through semi-permeable membrane and this phenomenon is called reverse osmosis.
Case Study Answers:
1. Answer :




2. Answer :





Class 12 Chemistry All Chapter Notes & Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Question Answer

