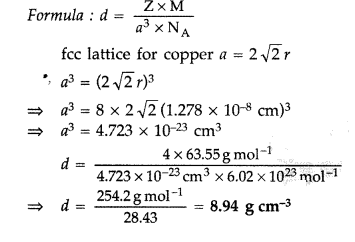Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Question Answer: Here we are providing Best Solution (Question & Answer) for class 12 Subject Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State. Students can make easily study access all the chapters of Class 12 Chemistry.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Question Answer
Multiple Choice questions-
- Close packing is maximum in the crystal which is
(a) bcc
(b) fee
(c) simple cubic
(d) end centred cubic
- In a solid lattice, the cation has left a lattice site and is located at an interstitial position. The lattice defect is
(a) n-type
(b) p-type
(c) Frenkel defect
(d) Schottky defect
- The coordination number of metal crystallizing in a hexagonal close packing structure are
(a) 12
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 10
- In a body centred unit cell, the number of atoms present is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
- In a trigonal crystal
(a) a = b = c, α = ß = γ ≠ 90°
(b) a = b ≠ c, α = ß = γ = 90°
(c) a ≠ b ≠ c, α = ß = γ = 90°
(d) a = b ≠ c, α = ß = 90°, γ = 120°
- The appearance of colour in solid alkali metal halides is generally due to
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Frenkel defect
(c) F-centre
(d) Interstitial position
- In a body centred cubic structure, the space occupied is about
(a) 74%
(b) 20%
(c) 68%
(d) 52.4%
- Some polar crystals when heated produce small electrical current. The phenomenon is called
(a) Ferroelectricity
(b) Anti-ferroelectricity
(c) Pyroelectricity
(d) Piezoelectricity.
- The empty space within hep arrangement is
(a) 34%
(b) 47.6%
(c) 32%
(d) 26%
- A crystal system with axes a ≠ b ≠ c and angles α ≠ ß ≠ γ ≠ 90° corresponds to
(a) monoclinic
(b) triclinic
(c) cubic
(d) tetragonal
- The number of Cl– ions present around each Na+ ion in NaCl crystal lattice is
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 6
- To get n-type semiconductor from silicon, it should be doped with an element having valence electrons of
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 5
- Volume occupied by atoms in fee is
(a) 74%
(b) 68%
(c) 52.4%
(d) 75%
- Percentage empty space in a bcc arrangement is
(a) 74%
(b) 68%
(c) 32%
(d) 26%
- To get p-type semiconductor, impurity to be added to silicon should have which of the following number of valence electrons?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 5
Very Short Question:
- Which point defect in crystals does not alter the density of the relevant solid?
- Which point defect in its crystal units alters the density of a solid?
- Which point defect in its crystal units increases the density of a solid?
- How do metallic and ionic substances differ in conducting electricity?
- Which point defect of its crystals decreases the density of a solid?
- What is the number of atoms in a unit cell of a face-centred cubic crystal?
- Write a feature which will distinguish a metallic solid from an ionic solid?
- What type of semiconductor is obtained when silicon is doped with arsenic?
- Write a distinguishing feature of metallic solids.
- What type of interactions hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid?
Short Questions:
- Iron has a body centred cubic unit cell with a cell edge of 286.65 pm. The density of iron is 7.87 g cm-3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number (At. mass of Fe = 56 g mol-1).
- Silver crystallises with face-centred cubic unit cells. Each side of the unit cell has a length of 409 pm. What is the radius of an atom of silver?
- The well known mineral fluorite is chemically calcium fluoride. It is known that in one unit cell of this mineral there are 4 Ca2+ ions and 8 F– ions and that Ca2+ ions are arranged in a fee lattice. The F– ions fill all the tetrahedral holes in the face centred cubic lattice of Ca2+ ions. The edge of the unit cell is 5.46 × 10-8 cm in length. The density of the solid is 3.18 g cm-3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number (Molar mass of CaF2 = 78.08 g mol-1).
- The density of copper metal is 8.95 g cm-3. If the radius of copper atom is 127.8 pm, is the copper unit cell a simple cubic, a body-centred cubic or a face centred cubic structure?
- Silver crystallises in face-centred cubic unit cells. Each side of the unit cell has a length of 409 pm. What is the radius of silver atom?
- Silver crystallizes in face-centered cubic unit cell. Each side of this unit cell has a length of 400 pm. Calculate the radius of the silver atom. (Assume the atoms just touch each other on the diagonal across the face of the unit cell. That is each face atom is touching the four comer atoms.)
- The density of lead is 11.35 g cm-3 and the metal crystallizes with fee unit cell. Estimate the radius of lead atom.
(At. Mass of lead = 207 g mol-1 and NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol-1)
- Tungsten crystallizes in body centred cubic unit cell. If the edge of the unit cell is 316.5 pm, what is the radius of tungsten atom?
- Iron has a body centred cubic unit cell with a cell dimension of 286.65 pm. The density of iron is 7.874 g cm-3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number. (At mass of Fe = 55.845 u)
- Copper crystallises with face centred cubic unit cell. If the radius of copper atom is 127.8 pm, calculate the density of copper metal.
(Atomic mass of Cu = 63.55 u and Avogadro’s number NA = 6.02 × 10223 mol-1)
Long Questions:
- (a) An element has an atomic mass 93 g mol-1 and density 11.5 g cm-3. If the edge length of its unit cell is 300 pm, identify the type of unit cell.
(b) Write any two differences between amorphous solids and crystalline solids.
- (a) Calculate the number of unit cells in 8.1 g of aluminium if it crystallizes in a f.c.c. structure. (Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol-1)
(b) Give reasons:
(i) In stoichiometric defects, NaCl exhibits Schottky defect and not Frenkel defect.
(ii) Silicon on doping with Phosphorus form n-type semiconductor.
(iii) Ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic substances.
Assertion and Reason Questions:
- In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements, and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements, but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement, but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement, but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: The number of tetrahedral voids is double the number of octahedral voids.
Reason: The size of the tetrahedral voids is half of that of the octahedral void.
- In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements, and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements, but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- Assertion is correct statement, but reason is wrong statement.
- Assertion is wrong statement, but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: bee and hep has same packing efficiency
Reason: bee arrangement has 2 atoms per unit cell, while fee has 4 atoms per unit cell.
Case Study Questions:
1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The idealized ionic solid consists of two interpenetrating lattices of oppositely-charged point charges that are held in place by a balance of coulombic force of long range. But real ions occupy space, no such “perfect” ionic solid exists in nature. Chemists usually apply the term “ionic solid” to binary compounds of the metallic elements of groups 1 – 2 with one of the halogen elements or oxygen. The most well known ionic solid is sodium chloride, also known by its geological names as rock-salt or halite. Structurally, each ion in sodium chloride is surrounded and held in tension by six neighbouring ions of opposite charge; this is known as (6, 6) coordination. The resulting crystal lattice is of a type known as simple cubic. There are many other fundamental ionic structures (not all cubic) and these are: Zinc blende structure (ZnS) : having ccp arrangement of S2– and Zn2+ in alternate tetrahedral voids; Wurtzite structure (ZnS) having hcp arrangement of S2– and Zn2+ in alternate tetrahedral voids; Fluorite structure (CaF2) having ccp arrangement of Ca2+ and F– in all tetrahedral voids Antifluorite structure (Na2O) having ccp arrangement of O2- and Na+ in all tetrahedral voids. These solids tend to be quite hard and have high melting points.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer.
- In NaCl crystal, each Cl– ion is surrounded by.
- 4 Na+ ions
- 6 Na+ ions
- 1 Na+ ion
- 2 Na+ ions
- In an antifluorite structure, cations occupy.
- Tetrahedral voids.
- Centre of cube
- Octahedral voids
- Corners of cube.
- Anti fluorite structure is derived from fluorite structure by.
- Heating fluorite crystal lattice.
- Subjecting fluorite structure to high pressure.
- Interchanging the positions of positive and negative ions in the lattice.
- None of these.
- In crystal structure of sodium chloride, the arrangement of Cl– ion is.
- fcc
- both fcc and bcc
- bcc
- None of these
- Ionic solid BaF2 has which kind of structure?
- Fluorite
- Antifluorite
- Wurtzite
- Rock-salt
2. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
In contrast to the disorders of gases and liquids, there is translational order in crystals. However, disordered or amorphous solids also exist which lack such order, they are really highly viscous liquids. In translational order entire structure or lattice, can be generated by repeated replication of a small regular figure, termed as unit cell. The planes of any crystalline structure can be specified using Miller indices, which is also serve to identify single crystal faces.The ordered structure, or lattice, of a solid can be determined by X-ray or neutron diffraction studies, in which a beam of X-rays of neutrons is scattered from the sample to produce a diffraction pattern which can be analyzed to reveal the crystal structure of the sample. All crystal lattices can be classified into 14 Bravais lattices belonging to 7 systems. For example, the simple cubic, face-centred cubic and body-centred cubic lattices are the 3 lattices of the cubic system. Cubic and hexagonal close-packed structures have the structure of tightly packed spheres, where each sphere touches 12 neighbours, 6 in the same plane and 3 above and 3 below. These two dose-packed structures differ in the placement of successive planes or layers. For the hexagonal close packing, a third layer is laid down to reproduce the first layer, so that the structure could be represented by ABABAB …. For cubic close packing, third layer is again displaced, corresponding to ABCABC.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
- In hexagonal close packing, a sphere has coordination number of.
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 12
- Which of the following arrangements correctly represents hexagonal and cubic close packed structure respectively?
- ABCABC…and ABAB…
- ABAB…and ABCABC…
- Both have ABAB … arrangement.
- Both have ABCABC… Arrangement.
- The arrangement of the first two layers, one above the other, in hep and ccp arrangements is.
- Exactly same in both cases
- Partly same and partly different
- Different from each other
- Nothing definite.
- Which of the following statements is not correct?
- The amorphous solids have a random, disordered arrangement of constituents.
- The simple cubic, face-centred and body-centred are the three lattices of the cubic system.
- The number of Bravais lattice in which a crystal can be categorized is 7.
- A metal that crystallizes in hep structure has coordination number 12.
- Which of the following statements about amorphous solids is incorrect?
- They melt over a range of temperature.
- There is no orderly arrangement of particles.
- They are anisotropic.
- They are rigid and incompressible.
Answers key
MCQ answers:
- (b) fee
- (c) Frenkel defect
- (a) 12
- (b) 2
- (a) a = b = c, α = ß = γ ≠ 90°
- (c) F-centre
- (c) 68%
- (c) Pyroelectricity
- (d) 26%
- (b) triclinic
- (d) 6
- (d) 5
- (a) 74%
- (c) 32%
- (b) 3
Very Short Answers:
- Frenkel defect.
- Schottky defect.
- Metal excess defect increases the density of a solid. It is due to presence of extra cations in the interstitial sites.
- The electrical conductivity in metallic substances is due to free electrons while in ionic substances the conductivity is due to presence of ions.
- Schottky defect.
- The number of atoms in a unit cell of fcc-crysta! is 4 atoms.
- The electrical conductivity in metallic solid is due to free electrons while in ionic solid the conductivity is due to presence of ions.
- n-type semiconductor.
- Metallic solids possess high electrical and thermal conductivity due to presence of free electrons.
- Dipole-dipole forces of attractions hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid.
Short Answers:
- Answer
a = 286.65 pm = 286.65 × 10-10,
d = 7.87 g cm-3, M = 56 g mol-1
Z = 2, NA = ?

∴ Avogadro’s number NA = 6.022 × 1023
- Answer
Given : a = 409 pm r = ?
For fee unit cell, the formula is a

∴ Radius of an atom of silver = 144.62 pm
- Answer
Edge of the unit cell (a) = 5.46 × 10-8 cm
Density (P) = 3.18 g cm-3
According to the formula

- Answer:
If copper atom were simple cubic :
a = 2 × r = 2 × 127.8 pm = 255.6 pm
= 255.6 pm = 255.6 × 10-10 cm
Z = 1

∴ P = 6.34 g cm-3
Actual density = 8.95 g cm-3
Hence copper atom is not simple cubic.
If copper atom were body-centred :

∴ P = 8.21 g cm-3
Hence, copper atom is not body centered
If copper atom were face-centered

Hence, copper is face-centred cubic.
5. Answer :
Given : a = 409 pm r =?
For fee unit cell, the formula is a

∴ Radius of an atom of silver = 144.62 pm
6. Answer
Given : a = 400 pm, r = ?

∴ Radius of the silver, r = 141.4 pm
7. Answer
Given : d = 11.35 g cm-3
According to the formula

8. Answer

9. Answer :

- Answer :
In fee, lattice, Z = 4 atoms [fee = face centred cubic]
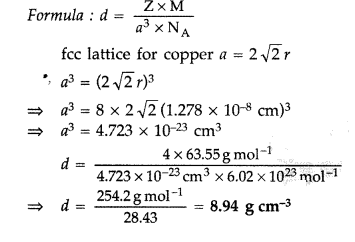
Long Answers:
- Answer
(a) Given:
M = 93 g mol-1; ρ = 11.5 g cm-3;
a = 300 pm = 300 × 10-10 cm = 3 × 10-8 cm
Using formula,

= 2.01 (approx.)
As the number of atoms present in given unit cells are coming nearly equal to 2, hence the given units cell is body centered cubic unit cell (BCC).
| Amorphous solids | Crystalline solids |
| (i) They are isotropic, i.e., they will show same value of physical perties in directions. | (i) They are anisotropic, i.e., tropic, i.e., value of physical properties will be different when measured along different directions. |
| (ii) They have short range order. | (ii) They have long range order. |
2. Answer
(a) Given:
Mass of Al = 8.1,
Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol-1
No. of atoms = η × 6.022 × 1023
= 8.127× 6.022 × 1023
= 0.3 × 6.022 × 1023
= 1.8066 × 1023
Since one f.c.c. unit cell has 4 atoms
∴ No. of unit cells = 1.8066×1023/4
= 4.5 × 1022 unit cells
(b) (i) Schottky defect is shown by the ionic solids having very small difference in their cationic and anionic radius whereas Frenkel defect is shown by ionic solids having large difference in their cationic and anionic radius. NaCl exhibits Schottky defect because radius of both Na+ and Cl– have very small difference.
(ii) Phosphorus is pentavalent that is it has 5 valence electrons, an extra electron results in the formation of n-type semi conductors on doping with Silicon. The conductivity is due to presence of extra electrons.
(iii) In antiferromagnetic substances the magnetic moments of domains are half aligned in one direction and remaining half in opposite direction in the presence of magnetic field so magnetic moment will be zero while in ferrimagnetic substances the magnetic moments of domains are aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers, hence shows some value of magnetic moment.

Assertion and Reason Answers:
1. (c) Assertion is correct statement, but reason is wrong statement.
Explanation:
The size of tetrahedral voids is smaller but not half of the octahedral voids.
2. (d) Assertion is wrong statement, but reason is correct statement.
Explanation:
bcc and hep have different arrangements of particles. bcc has 68% and hcp has 74% packing efficiency.
Case Study Answers:
1. Answer :
- (b) 6 Na+ ions
Explanation:
In NaCl crystal, each Cl– ion is surrounded by 6 Na+ ions.
- (a) Tetrahedral voids.
Explanation:
Anti-fluorite structure (NaCl) have ccp arrangement of O2- and Na+ in all tetrahedral voids.
- (c) Interchanging the positions of positive and negative ions in the lattice.
Explanation:
Antifluorite structure is derived from fluorite structure by interchanging the positions of positive and negative ions.
- (a) fcc
Explanation:
In NaCl crystal structure, Cl– ions form fcc.
- (a) Fluorite
Explanation:
BaF2 has fluorite structure.
2. Answer :
- (d) 12
Explanation:
For hcp packing, the coordination number of each sphere is 12 (6 in its own layer, 3 in the upper layer and 3 in the lower layer).
- (b) ABAB …. and ABCABC…
Explanation:
In hexagonal close packing, each sphere of third layer lies exactly above the sphere of first layer. Thus, hep is abbreviated as ABAB …. In cubic close packing, the spheres of third layer do not come over those of first layer and spheres of fourth layer correspond with those in first layer. Thus, it is represented as AB CAB C…
- (a) Exactly same in both cases.
- (c) The number of Bravais lattice in which a crystal can be categorized is 7.
Explanation:
The number of Bravais lattice in which a crystal can be categorized is 14.
- (c) They are anisotropic.
Explanation:
They are isotropic as they show same properties in all directions.
Class 12 Chemistry All Chapter Notes & Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Isolation of Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The D And F Block Elements Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Question Answer
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Question Answer