Class 12 Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Question Answer: Explore comprehensive question-answer solutions for Class 12 Chapter 9 on Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production. Prepare for exams with detailed explanations, examples, and key insights covering topics such as plant breeding, tissue culture, genetic engineering, and sustainable agricultural practices to enhance food production and meet the growing global demand.
Class 12 Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Question Answer
- Multiple Choice Questions:
- The chances of contracting bird flu from a properly cooked (above 100°C) chicken and egg are:
- very high
- high
- moderate
- none.
- A group of animals which are related by descent and share many similarities are referred to as:
- breed
- race
- variety
- species.
- Inbreeding is carried out in animal husbandry because it:
- increases vigour
- improves the breed
- increases heterozygosity
- increases homozygosity.
- Question 4. Which one of the following is a marine fish?
- Rohu
- Hilsa
- Catla
- Common carp.
- Which one of the following products of apiculture is used in cosmetics and polishes?
- Honey
- Oil
- Wax
- Royal jelly.
- More than 70 percent of livestock population is in:
- Denmark
- India
- China
- India and China.
- The agriculture sector of India employs:
- 60 per cent of the population
- 70 per cent of the population
- 30 per cent of the population
- 62 per cent of the population
- 33 per cent of India’s Gross Domestic Product comes from
- industry
- agriculture
- export
- small-scale cottage industries.
- Sonalika and Kalyan Sona are varieties of:
- wheat
- rice
- millet
- tobacco.
- Which one of the following is not a fungal disease?
- Rust of wheat
- Smut of Bajra
- Black rot of crucifers
- Red rot of sugarcane.
- In virus-infected plants the meristematic tissues in both apical and axillary buds are free of virus because:
- the dividing cells are virus resistant
- meristems have anti-viral compounds
- the cell division of meristems is faster than the rate of viral multiplication
- viruses cannot multiply within meristem cell (s).
- Several South Indian states raise 2-3 crops of rice annually. The agronomic feature that makes this possible is because of:
- shorter rice plant
- better irrigation facilities
- early yielding rice variety
- disease-resistant rice variety.
- Which one of the following combinations would a sugarcane farmer look for in the sugarcane crop?
- Thick stem, long internodes, high sugar content and disease resistant
- Thick stem, high sugar content and profuse flowering
- Thick stem, short internodes, high sugar content, disease resistant
- Thick stem, low sugar, content, disease resistant.
- Fungicides and antibiotics are chemicals that:
- enhance yield and disease resistance
- kill pathogenic fungi and bacteria, respectively
- kill all pathogenic microbes
- kill pathogenic bacteria and fungi respectively.
- Use of certain chemicals and radiation to change the base sequences of genes of crop plants is termed:
- recombinant DNA technology
- transgenic mechanism
- mutation breeding
- gene therapy.
- Very Short Question:
- Why is inbreeding necessary in animal husbandary?
- Name two fungal diseases of Crop plants.
- Which product of Apiculture is used in cosmetics and polishes?
- Semi-dwarf varieties of a crop plant were derived from IR-8. Name that crop.
- Write two qualities of Saccharum officinarum (Sugarcane) grown in South India.
- Name any two semi – dwarf varieties of wheat introduced into all wheat growing places of India?
- What is Biofortification?
- Give an example where mutation breeding has been Successfully carried out for introducing disease resistance.
- Name two better yielding varieties of rice developed in India?
- Name the microbe that is grown for use as protein – rich food?
- Short Questions:
- Why are proteins synthesized from Spirulina called Single celled Proteins? What is the significance of such a protein?
- Differentiate between inbreeding and outbreeding in animals.
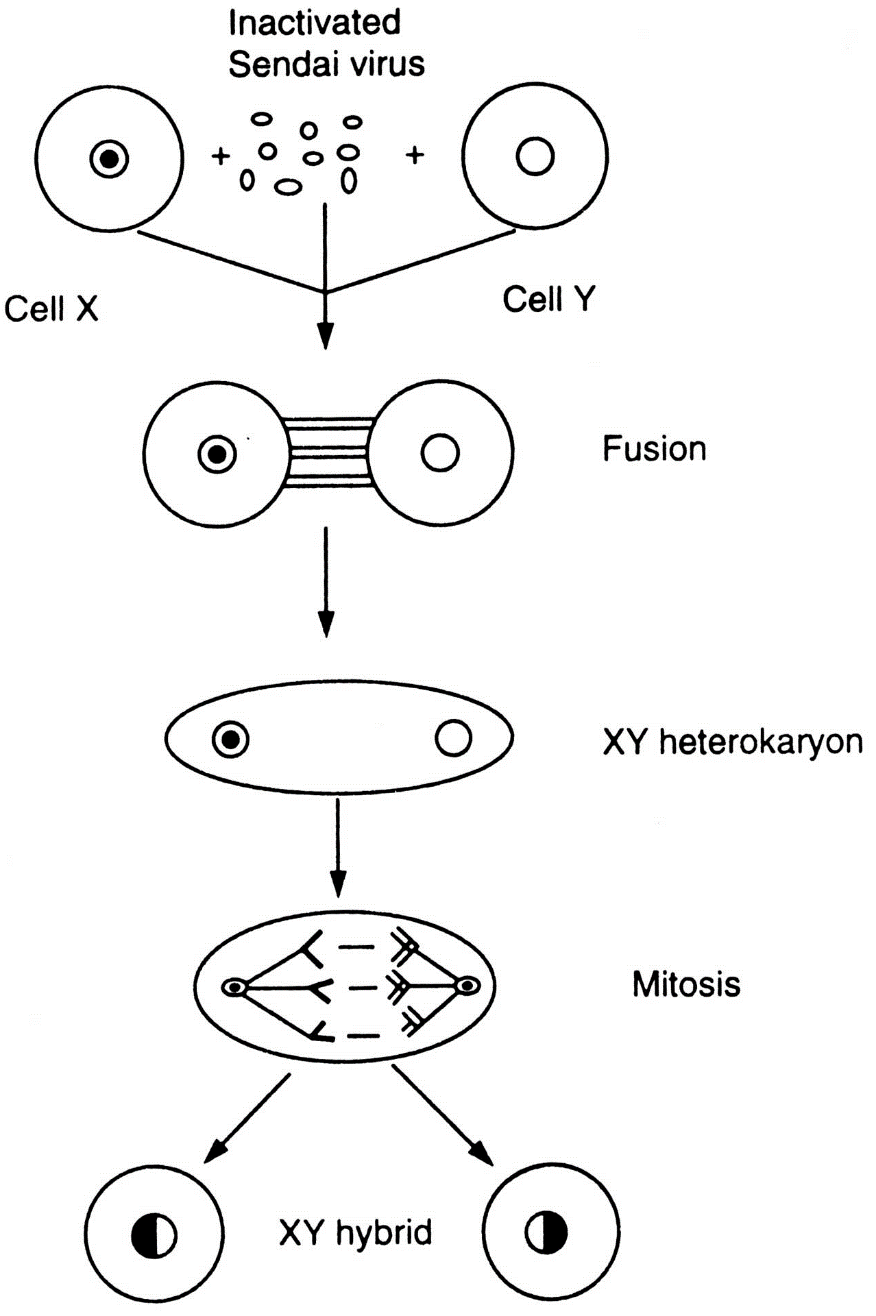
- Observe the process of Somatic hybridisation given below and fill in the blanks. (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)

- What is single cell protein? What is its significance?
- Expand MOET. How is it carried out?
- What is germplasm? Why is it necessary to have gemplasm collection?
- What is inbreeding depression? Why do self – pollinated crops do not show the ill-effects of inbreeding depression?
- What is interspecific hybridization. Give an example?
- Long Questions:
- What is a hybrid? Explain the procedure of obtaining a hybrid.
- “The benefits of a new variety can be achieved only if farmers grow the variety”. Explain.
- Discuss the role of plant tissue culture in increasing food production.
- Assertion & Reason Questions:
- For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Fish meal is a rich source of protein for cattle and poultry.
Reason: Fish meal is produced from non-edible parts of fishes like fins, tail etc.
- For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: In case of vegetatively propagated crops, pure-line selection is not required.
Reason: Hybrid vigour is mostly used in vegetatively propagated plants.
- Case Study Questions:
- Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Dairying is the management of animals for milk and its products for human consumption. Can you list the animals that you would expect to find in a dairy? What are different kinds of products that can be made with milk from a dairy farm? In dairy farm management, we deal with processes and systems that increase yield and improve quality of milk. Milk yield is primarily dependent on the quality of breeds in the farm. Selection of good breeds having high yielding potential (under the climatic conditions of the area), combined with resistance to diseases is very important. For the yield potential to be realised the cattle have to be well looked after – they have to be housed well, should have adequate water and be maintained disease free. The feeding of cattle should be carried out in a scientific manner – with special emphasis on the quality and quantity of fodder. Besides, stringent cleanliness and hygiene (both of the cattle and the handlers) are of paramount importance while milking, storage and transport of the milk and its products. Nowadays, of course, much of these processes have become mechanised, which reduces chance of direct contact of the produce with the handler. Ensuring these stringent measures would of course, require regular inspections, with proper record keeping.
It would also help to identify and rectify the problems as early as possible. Regular visits by a veterinary doctor would be mandatory. You would probably find it interesting if you were to prepare a questionnaire on diverse aspects of dairy keeping and then follow it up with a visit to a dairy farm in your locality and seek answers to the questions.
1) In the animals, ………………………. Is the management for milk and milk products (For human consumption).
- Farming
- Breeding
- Culturing
- Dairying
2) In the farm, milk yield is primarily depends on the quality of
- Breed
- Soil
- Plants
- Grass
3) Selection of good breed results in
- High crop yield
- High area
- High farm
- High milk yield
4) How to maintain yield potential?
5) What is important during milking and transportation of milk.
- Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Bee-keeping or apiculture is the maintenance of hives of honeybees for the production of honey. It has been an age-old cottage industry. Honey is a food of high nutritive value and also finds use in the indigenous systems of medicine. Honeybee also produces beeswax, which finds many uses in industry, such as in the preparation of cosmetics and polishes of various kinds. The increased demand of honey has led to large-scale beekeeping practices; it has become an established income generating industry, whether practiced on a small or on a large scale. Bee-keeping can be practiced in any area where there are sufficient bee pastures of some wild shrubs, fruit orchards and cultivated crops. There are several species of honeybees which can be reared. Of these, the most common species is Apis indica. Beehives can be kept in one’s courtyard, on the verandah of the house or even on the roof. Bee-keeping is not labour-intensive. Bee-keeping though relatively easy does require some specialised knowledge and there are several organisations that teach bee-keeping.
The following points are important for successful bee-keeping: (i) Knowledge of the nature and habits of bees, (ii) Selection of suitable location for keeping the beehives, (iii) Catching and hiving of swarms (group of bees), (iv) Management of beehives during different seasons, and (v) Handling and collection of honey and of beeswax. Bees are the pollinators of many of our crop species (see chapter 2) such as sunflower, Brassica, apple and pear. Keeping beehives in crop fields during flowering period increases pollination efficiency and improves the yield–beneficial both from the point of view of crop yield and honey yield
1) Which of the following are pollinators of pear, sunflower, Brassica, and apple like crop species?
- Bees
- Scorpions
- Spiders
- Lice
2) Apiculture of Bee-keeping is the process where maintenance of …………………….. occurs.
- Nests
- Shells
- Hives
- None of these
3) A food that have high nutritive value is ………………… in the apiculture
- Curd
- Mushroom
- Honey
- Milk
4) Write any three successful ways of bee-keeping.
5) What does honey bee produce?
- Answer Key-
- Multiple Choice Answers:
- (d) none.
- (a) breed
- (d) increases homozygosity.
- (b) Hilsa
- (c) Wax
- (d) India and China.
- (d) 62 per cent of the population
- (b) agriculture
- (a) wheat
- (c) Black rot of crucifers
- (c) the cell division of meristems is faster than the rate of viral multiplication
- (c) early yielding rice variety
- (a) Thick stem, long internodes, high sugar content and disease resistant
- (b) kill pathogenic fungi and bacteria, respectively
- (c) mutation breeding
- Very Short Answers:
- Inbreeding increases homozygosity.
- Brown rust of wheat, Smut of wheat, red rot of Sugar cane, Late blight of potato.
- Beewax.
- Paddy crop (rice)
- Thicker stem and higher sugar content.
- Sonalika & Kalyan sona.
- The breeding of crops to increase the levels of vitamins, minerals & higher proteins & healthier fats content is called biofortification.
- varieties of mung bean have been successfully developed that are resistant to yellow mosaicvirus & powdery mildew.
- Jaya & Ratna
- Methylophilus methylotropous.
- Short Answer:
- The protein rich food produced by microbes is called as single called protein (SCP) Spirulina is a microorganisms which has more protein. It is a quick method of protein production because the growth rate of microbes is enormous. Hence, it provides a protein rich diet for human beings.
- When breeding is between animals of the same breed, it is callednbreeding, while cross between different breeds in called out breeding.
- Ans.
i. Isolation of protoplast of Tomato cell and Potato cell.
ii. Somatic hybridisation.
iii. Pomato
iv. Somatic hybrid
- The production of edible proteins on a large scale from microorganisms for human beings &animals is called Single cell protein. It is important because:
i. It provide protein – rich supplement in diet.
ii. It reduces pressure on agriculture for supply of desired proteins.
iii. It helps to minimise environmental pollution
- Moet is multiple ovulation Embryo transfer. It involves following steps:
i. A cow is administered hormones to induce follicular motivation & super ovulation.
ii. Cow is mated with a selected bull.
iii. Fertilized eggs at 8-32 celled stage are recovered & transferred to surrogate mother.
- The sumtotal of all the alleles of the gene present in a plant & its relative is called Germplasm. Germplasm collection is very essential for effective exploitation of natural genes available in the population.
- Continued inbreeding especially close inbreeding usually reduces fertility & even productivity.This is called inbreeding depression. In self – pollinated crops, since the male & female reproductiveparts are of the same flower & are compatible with each other to cause fertilisation: it does notshow ill – effects of inbreeding depression.
- It is a method of outbreeding in which male & female animal of two different species are crossed to combine the desirable features of both the parents into one eg, mule is produced by a cross between donkey & a female horse.
- Long Answer:
- Hybrid: A progeny obtained by crossing two varieties or species having desired genes thus showing required characters.
Process of hybridization: This technique involves the following steps,
- Removal of undehisced anthers from the bisexual flower of a plant to be used as female. This is called emasculation.
- The emasculated flowers are covered by butter paper to avoid pollination by an undesirable pollen grain. It is also termed bagging.
- Pollen grains from known seeds of desirable plants are used to pollinate these emasculated flowers.
- They are collected, multiplied and their desirable characters are determined.
- The seed of new variety must be multiplied and made available to the farmers. In-plant breeding, seed means any plant part that is used to grow a crop. Thus ‘seed’ would include grains of wheat, rice, etc. tubers of the potato, stems of sugarcane, etc., provided they are used for producing new plants.
Therefore, wheat grains used as food cannot be termed as seeds, whereas those used for raising a crop are called seeds. A seed of a variety with superior traits is called an improved seed, which must be of high purity and have a high germination percentage. It must also be free from weed seeds and from diseases.
- Applications of tissue culture technique:
- This technique is applied for the rapid multiplication of desirable and rare plants.
- By this technique, an indefinite number of plants can be produced.
- From the culturing of virus-free tissues of the shoot apex of an infected plant, it becomes possible to obtain virus-free plant in sufficient stock. The tissue culture technique has been used to obtain virus-free potatoes and sugarcane.
- The technique (Embryo culture) is useful in overcoming seed dormancy, but also in producing viable plants from the crosses which normally fail due to the death of immature embryos.
- The technique has been applied for obtaining a large number of haploid and homozygous diploids.
- Somatic hybridization helps the fusion of cells belonging to different families.
This technique is also useful for the genetic improvement of useful plants.
- Assertion and Reason Answers:
1) c) Assertion is true, but reason is false
Explanation:
Fish meal is prepared from the wastes of fish oil or canning industry or from the whole fish of nol-oil-type. Wastes of cod industry are known as white ‘fish meal’. The protein content of this meal is highly digestible, nutritive and is of biological importance. This fish meal also contains calcium phospholipids, and iodine, fish meal is also used as major food of domestic animals like pigs, poultry and cattle.
2) b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
In case of vegetatively propagated crops, pure line selection is not required. Pureline selection is useful only for sexually reproducing plants. Hybrids vigour is most profitably used in vegetatively propagated crops because they do not involve sexual reproduction and hence loss of hybrid superiority
- Case Study:
1.
- 1)(d) Dairying.
- (a) Breed
- (d) High milk yield
- Cattles should be disease free, should provide adequate water, and should housed well etc., by this way yield potential is maintained.
- Hygiene and cleanliness is important during milking and transportation of milk.
- (a) Bees.
- (c) Hives.
- (c) Honey.
- The successful ways of bee-keeping include beehive keeping in selected suitable location, Honey and beeswax collection, catching of swarms, hiving of swarms, and proper management of hives in various seasons.
- Honey bee can produce honey (Has high nutritive value) and beeswax (Useful in cosmetic).
Class 12 Biology All Chapter Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Question Answer
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Notes
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question Answer
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes Question Answer
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Notes
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Question Answer
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Notes
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question Answer
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Notes
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question Answer
- Chapter 7 Evolution Notes
- Chapter 7 Evolution Question Answer
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Notes
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Question Answer
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Notes
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Question Answer
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Notes
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Question Answer
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Notes
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Question Answer
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Notes
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Question Answer
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Notes
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Question Answer
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Notes
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Question Answer
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Notes
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Question Answer
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Notes
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Question Answer