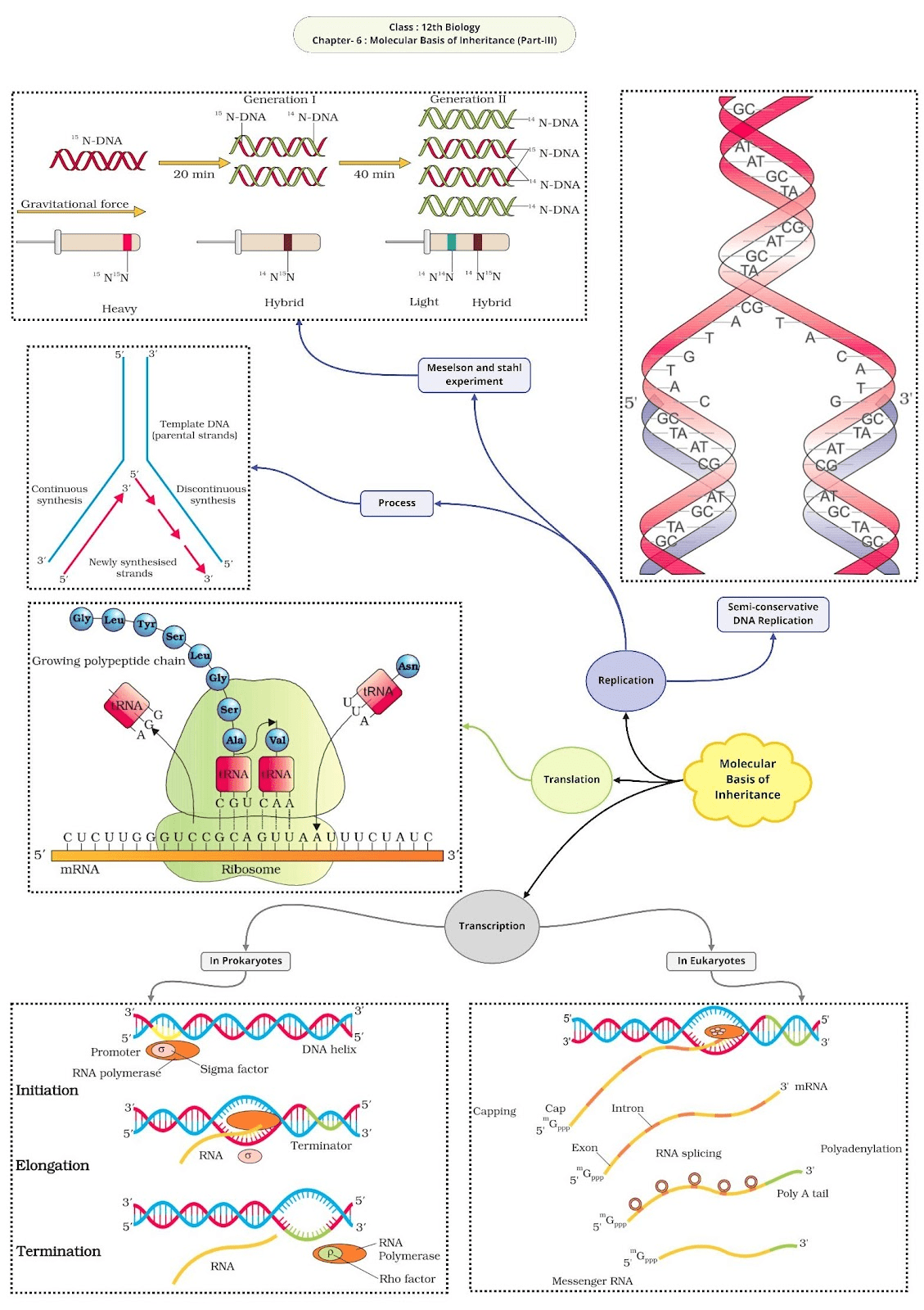
Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question Answer: Explore comprehensive question-answer solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 on Molecular Basis of Inheritance. Prepare for exams with detailed explanations, examples, and key insights covering topics such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, gene regulation, and biotechnology.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question Answer
- Multiple Choice Questions:
- Who proved semiconservative mode of DNA replication for the first time in E. coli with the help of N15 heavy nitrogen isotope?
- Watson and Crick
- Kornberg and Ochova
- Messelson and Stahl
- Luria and Delbruck
- A nucleoside differs from a nucleotide. It lacks the:
- base
- sugar
- phosphate group
- hydroxyl group.
- Both deoxyribose and ribose belong to a class of sugars called:
- trioses
- hexoses
- pentoses
- polysaccharides.
- The fact that a purine base always paired through hydrogen bonds with a pyrimidine base leads to, in the DNA double helix:
- the antiparallel nature
- the semiconservative nature
- uniform width throughout DNA
- uniform length in all DNA.
- The net electric charge on DNA and histones is:
- both positive
- both negative
- negative and positive, respectively
- zero
- The promoter site and the terminator site for transcription are located at:
- 3’ (downstream) end and 5’ (upstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
- 5’ (upstream) end and 3’ (downstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
- the 5’ (upstream) end
- the 3’ (downstream) end.
- Which of the following statements is the most appropriate for sickle cell anaemia?
- It cannot be treated with iron supplements.
- It is a molecular disease.
- It confers resistance of acquiring malaria.
- All of the above.
- One of the following is true with respect to AUG
- It codes for methionine only.
- It is also an initiation codon.
- It codes for methionine in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
- All of the above.
- The first genetic material could be:
- protein
- carbohydrates
- DNA
- RNA.
- With regard to mature mRNA in eukaryotes:
- exons and introns do not appear in the mature RNA
- exons appear but introns do not appear in the mature RNA
- introns appear but exons do not appear in the mature RNA
- both exons and introns appear in the mature RNA.
- The human chromosome with the highest and least number of genes in them are respectively:
- Chromosome 21 and Y
- Chromosome 1 and X
- Chromosome 1 and Y
- Chromosome X and Y.
- Who amongst the following scientists had no contribution in the development of the double helix model for the structure of DNA?
- Rosalind Franklin
- Maurice Wilkins
- Erwin Chargaff
- Meselson and Stahl.
- DNA is a polymer of nucleotides which are linked to each other by 3’-5’ phosphodiester bond. To prevent polymerisation of nucleotides, which of the following modifications would you choose?
- Replace purine with pyrimidines
- Remove/Replace 3’ OH group in deoxyribose
- Remove/Replace 2’ OH group with some other group in deoxyribose
- Both ‘B’ and ‘C’.
- Which of the following steps in transcription is catalysed by RNA polymerase?
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
- All of the above.
- Control of gene expression takes place at the level of:
- DNA-replication
- Transcription
- Translation
- None of the above
- Very Short Question:
- Name the factors for RNA polymerase enzyme which recognises the start and termination signals on DNA for transcription process in Bacteria.
- Mention the function of non-histone protein.
- During translation what role is performed by tRNA
- RNA viruses mutate and evolve faster than other viruses. Why?
- Name the parts ‘X’ and ‘Y’ of the transcription unit given below.
- Mention the dual functions of AUG.
- Name the process in which unwanted mRNA regions are removed & wanted regions are joined.
- Give the initiation codon for protein synthesis. Name the amino acid it codes for?
- In which direction, the new strand of DNA synthesised during DNA replication.
- What is the function of amino acyl tRNAsynthetase.
- Short Questions:
- Give two reasons why both the strands of DNA are not copied during transcription.
- Mention any two applications of DNA fingerprinting.
- State the 4 criteria which a molecule must fulfill to act as a genetic material.
- “DNA polymerase plays a dual function during DNA replication” comment on statement?
- Three codons on mRNA are not recognised by tRNA what are they? What is the general term used for them what is their significance in protein synthesis?
- Give two reasons why both the strands of DNA are not copied during DNA transcription?
- Why is it essential that tRNA binds to both amino acids & mRNA codon during protein synthesis?
- Explain what happens in frameshift mutation? Name one disease caused by the disorder?
- Long Questions:
- Write a note on messenger RNA.
- What is genetic code? List the properties of genetic code.
- What is the role of ribosomes during translation? Ribosomes move along mRNA molecules and catalyze the assembly of amino acids into protein chambers.
- Assertion and Reason Questions:
1. For question, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false
Assertion: Regulator and operator genes are not associated with constitutive genes
Reason: Constitutive genes need not be repressed.
2. For question, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false
Assertion: Lactose in lac operon is promoter gene.
Reason: Lactose inactivates the repressor gene.
- Case Study Questions:
1. Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
RNA or ribonucleic acid is a single chain polyribonucleotide which functions as carrier of coded genetic or hereditary information from DNA to cytoplasm for taking part in protein and enzyme synthesis. Six types of RNAs are ribosomal, transfer, messenger, genomic, small nuclear and small cytoplasmic RNA. Out of these, rRNA, mRNA and tRNA are major classes of RNAs that are involved in gene expression.
- Which one is referred to a soluble RNA?
- mRNA
- tRNA
- rRNA
- hnRNA
- The RNA that picks up specific amino acid from amino acid pool in the cytoplasm to ribosome during protein synthesis is?
- rRNA
- hnRNA
- mRNA
- tRNA
- Which of the following is found in both DNA and messenger RNA?
- Double helix structure
- Ribose
- Sugar-phosphate chain
- Thymine
- Which of the following statements regarding RNA is correct?
- Messenger RN As carries coded information for synthesis of polypeptide.
- Ribosomal RNAs bind with tRNA to catalyse the formation of phosphodiester bonds.
- Genomic RNA is always single stranded.
- Synthesis of rRNA occurs in cytoplasm by RNA polymerase III
- In studying a virus, you find the following proportions of nitrogenous bases present: adenine 23%, guanine 37%, cytosine 23% uracil 17%. Which of the following statement(s) regarding this virus is/are correct?
- It probably uses RNA as its genetic material.
- The genetic material of this virus is probably single stranded.
- Base pairing rules in virus in this virus include adenine: cytosine.
- I only
- I and II only
- II and III only
- All of these.
2. Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
DNA fingerprinting is a technique of determining nucleotide sequences of certain areas of DNA which are unique to each individual. Each person has a unique DNA fingerprint. Each fingerprint is the same for every cell, tissue and organ of a person. DNA fingerprinting is the basis of paternity testing in case of disputes.
- The technique developed to identify a person with the help of DNA restriction analysis is known as.
- DNA profiting
- DNA fingerprinting
- RFLP
- Both (a) and (b).
- For DNA fingerprinting, DNA is obtained from.
- Blood
- Hair root cells
- Semen
- All of these
- During DNA fingerprinting, the radioactive probes.
- Hybridise with DNA sample to form double stranded structure
- Egrade the DNA
- Create positive charge on DNA
- Cut the DNA sample at various sites.
- In India, DNA fingerprinting technique was developed by?
- Dr. Lalji Singh
- Alec Jeffreys
- Dr. Khorana
- None of these.
- Which of the following is true about DNA fingerprinting?
- VNTR is used as probe.
- DNA samples are loaded on agarose gel electrophoresis.
- It is based on identification of nucleotide sequence present on the DNA molecule.
- All of these
- Answer Key-
- Multiple Choice Answers:
- (c) Messelson and Stahl
- (c) phosphate group
- (c) pentoses
- (c) uniform width throughout DNA
- (c) negative and positive, respectively
- (b) 5’ (upstream) end and 3’ (downstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
- (d) All of the above.
- (d) All of the above.
- (d) RNA.
- (b) exons appear but introns do not appear in the mature RNA
- (c) Chromosome 1 and Y
- (d) Meselson and Stahl.
- (b) Remove/ Replace 3’ OH group in deoxyribose
- (b) Elongation
- (b) Transcription
- Very Short Answers:
- Sigma (s) factor and Rho(p) factor)
- Packaging of chromatin
- (i) Structural role
(ii) Transfer of amino acid.
- -OH group is present on RNA, which is a reactive group so it is unstable and mutate faster.
- X – Template strand, Y – Terminator.
- (i) Acts as initiation codon for protein synthesis
(ii) It codes for methionine.
- RNA splicing.
- Initiation codon – AUG & it code for methionine.
- 5’→→ 3
- Amino acyl tRNAsynthetasecatalyses activation of amino and attachment of activated amino acids to the 3-end of specific tRNA molecule.
- Short Answer:
- (a) If both the strands act as a template, they would code for RNA with different sequences. This in turn would code for proteins with different amino acid sequences. This would result in one segment of DNA coding for two different proteins, hence complicate the genetic information transfer machinery.
(b)If two RNA molecules were produced simultaneously, double stranded RNA complementary to each other would be formed. This would prevent RNA from being translated into proteins.
- Ans.
(i) To identify criminals in the forensic laboratory.
(ii) To determine the real or biological parents in case of disputes.
(iii) To identify racial groups to rewrite the biological evolution. (Any two)
- Ans.
(i) It should be able to generate its replica.
(ii) Should be chemically and structurally stable.
(iii) Should be able to express itself in the form of Mendelian characters.
(iv) Should provide the scope for slow changes (mutations) that are necessary for evolution.
- DNA polymerase plays a dual function –it helps in synthesis of new strand & also helps in proof reading i.e replacement of RNA strands lay DNA fragments.
- UAG UAA & UGA are the three codons that are not recognised by tRNA these are known as stop codon or non-sense codon. Since these three codons are not recognised by any tRNA they help in termination of protein chain during translation.
- (i) If both the strands code for RNA two different RNA molecules & two different proteins wouldbe formed hence genetic machinery would become complicated
(ii) Since the two RNA molecules would be complementary to each other, they would wind togetherto form dsRNA without carrying out translation which means process of transcription would befutile
- It is essential that tRNA binds to both amino acids & mRNA codon because tRNA acts as an adapter molecule with picks up a specific activated aminoacid from the cytoplasm & transferred it to the ribosomal in the cytoplasm where proteins are synthesized. It attracts itself to ribosome with the sequence specified by mRNA & finally it transmits its amino acid to new polypeptide chain.
- Frameshift mutation is a type of mutation where addition or deletion of one or two bases changes the reading from the site of mutation, resulting in protein with different set of amino acid.
- Long Answer:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA).
It forms only 5% of total RNA but is the longest of all. It brings instructions from DNA for the formation of a particular polypeptide. The instructions are coded in the form of a base sequence called genetic code. Three adjacent nitrogen bases specify a particular amino acid. The formation of polypeptides occurs over the ribosomes. mRNA gets attached to ribosomes.

mRNA.
It starts as a cap for attachment with the ribosome. It is followed by an initiation codon (AUG) either immediately or after a small non-coding region. It is followed by the coding region followed by the termination codon (UAA, UAG, and UGA). Then there is a small non-coding region and poly-A area at 3 termini. The mRNA may specify only a single polypeptide or a number of them called monocistronic and polycistronic respectively.
The life span of mRNA maybe a few minutes to an hour or even days in the case of RBC.
- The code language of DNA and mRNA is complementary. So, genetic code is the sequence of nucleotides in DNA and RNA that determines the amino acid sequence in proteins. Some amino acids are specified by more than one codon. The sequence of nucleotide on the tRNA molecule which complements the codon is called anticodon, e.g. one of the codons for the amino acid leucine is CUG and the anticodon is GAC. Similarly, the codon for phenylalanine is UUU, while the anticodon is AAA.
Properties of genetic code:
The following properties of genetic code have now been proved by experimental evidence.
- The code is a triplet.
- The code is degenerate.
- The code is non¬overlapping.
- The code is commaless.
- The code is non-ambiguous.
- The code is universal,
- Collinearity.
Both polypeptide and DNA or mRNA have a linear arrangement of their components.
The term code letter stands for a nucleotide A, T, G, or C in DNA and A, U, G, or C in RNA. The sequence of three does not code for any amino acid, such codons are called a non-sense codon, e.g. UGA.
- Role of ribosomes: Ribosomes usually form linear or helical groups during active protein synthesis called polyribosomes or polysomes. The mRNA strand having coded information joins along with smaller subunits of ribosomes. The adjacent ribosomes are 360 A apart.
The different parts of the ribosome connected with protein synthesis are:
- A tunnel for mRNA.
- A groove for the passage of newly synthesized polypeptide (larger subunit).
- Two active sites (P-site-peptidyl transfer or donor site and A-site or aminoacyl or acceptor site).
- A binding site for tRNA near A-site.
- Presence of enzyme peptidyl transferase.
- Recognition point of smaller subunit for mRNA.
- Presence of GTP-ase, binding sites for elongation factors, and translocases.
- Assertion and Reason Answers:
1. (a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Regulator gene controls the operator gene in cooperation with a chemical compound called inducer present in the cytoplasm. The regulation gene codes for and produce a protein substance called repressor. The repressor substance combines with the operator gene to repress its function. Therefore it is called regulator gene. The constitutive genes keep on functioning all the time. They need not be repressed. Therefore, the regulator and operator genes are not associated with them.
2. (a) Both assertion and reason are false
Explanation:
Lactose is not a promotor gene but an inducer of lac operon as it combines with repressor protein fanned by repressor or regulatory gene and not the gene itself. The inducer joins the repressor, forming a repressor-inducer complex. This complex prevents the repressor from binding with the operator gene of the operon. This frees the operator gene so that the RNA polymerase can move from the promoter to the structural genes. The structural genes are then transcribed, forming a piece of polycistronic mRNA. The latter is transcribed by tRNA and ribosomes into enzymes.
- Case Study Answers:
- (b) tRNA
Explanation:
tRNA is also referred to as soluble RNA (sRNA) because it cannot be easily separated even by ultra centrifugation technique.
- (d) tRNA
Explanation:
tRNA carries specific type of amino acid at CCA end to the ribosome during protein synthesis. It places the required amino acid properly in the sequence and translates the coded message of mRNA in terms of amino acids
- (c) Sugar-phosphate chain
Explanation:
The double helix structure is only found in DNA. Ribose is only found in mRNA, DNA has deoxyribose sugar instead. Thymine is found only in DNA, uracil replaces thymine in mRNA. Only the sugar-phosphate backbone is found common in both
- (a) Messenger RN As carries coded information for synthesis of polypeptide.
Explanation:
Ribosomal RNA is made in the nucleus. Ribosomal RNA binds with proteins to form large and small ribosomal subunits which combine to form ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Genomic RNA may be single stranded or double stranded. It is fragmented in influenza virus. Synthesis of rRNA occur in nucleolus.
- (b) I and II only
Explanation:
Uracil is present in this virus. So, RNA is the genetic material. The genetic material is not double stranded as the percentage of guanine and cytosine are not equal. Bases do not pair in single stranded viruses.
2.
- (d) Both (a) and (b).
- (d) All of these
Explanation:
For DNA fingerprinting, DNA is obtained from blood, semen, hair roots, tissue samples, nuclei of white blood cells or of spermatozoa, body secretions, etc.
- (a) Hybridise with DNA sample to form double stranded structure
Explanation:
In DNA fingerprinting, during hybridisation the bands are flooded with single stranded radioactive DNA probe. This single stranded DNA probe and sample DNA hybridise to form double stranded structure due to natural affinity.
- (a) Dr. Lalji Singh
Explanation:
In India, DNA fingerprinting technique was developed by Dr. Lalji Singh.
- (d) All of these
Class 12 Biology All Chapter Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Question Answer
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Notes
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question Answer
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes Question Answer
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Notes
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Question Answer
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Notes
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question Answer
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Notes
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question Answer
- Chapter 7 Evolution Notes
- Chapter 7 Evolution Question Answer
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Notes
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Question Answer
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Notes
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Question Answer
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Notes
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Question Answer
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Notes
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Question Answer
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Notes
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Question Answer
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Notes
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Question Answer
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Notes
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Question Answer
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Notes
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Question Answer
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Notes
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Question Answer