Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Question Answer: Explore comprehensive question-answer solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 on Ecosystem. Prepare for exams with detailed explanations, examples, and key insights covering topics such as ecological relationships, energy flow, nutrient cycling, and conservation of ecosystems to gain a deep understanding of the complex dynamics of the natural world.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Question Answer
- Multiple Choice Questions:
- An inverted pyramid of biomass can be found in which ecosystem?
- Forest
- Marine
- Grassland
- Tundra.
- Which of the following is not a producer?
- Spirogyra
- Agaricus
- Volvox
- Nostoc.
- Which of the following ecosystems is most productive in terms of net primary production?
- Deserts
- Tropical rainforests
- Oceans
- Estuaries.
- Pyramid of numbers is:
- Always upright
- Always inverted
- Either upright or inverted
- Neither upright nor inverted.
- Approximately how much of the solar energy that falls on the leaves of a plant is converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis?
- Less than 1%
- 2-10%
- 30%
- 50%.
- Among the following, where do you think the process of decomposition would be the fastest?
- Tropical rainforest
- Antarctic
- Dry arid region
- Alpine region.
- How much of the net primary productivity of a terrestrial ecosystem is eaten and digested by herbivores?
- 1%
- 10%
- 40%
- 90%.
- During the process of ecological succession the changes that take place in communities are:
- Orderly and sequential
- Random
- Very quick.
- Not influenced by the physical environment
- Climax community is in a state of:
- non-equilibrium
- equilibrium
- disorder
- constant change.
- Among the following biogeochemical cycles which one does not have losses due to respiration?
- Phosphorus
- Nitrogen
- Sulphur
- All of the above.
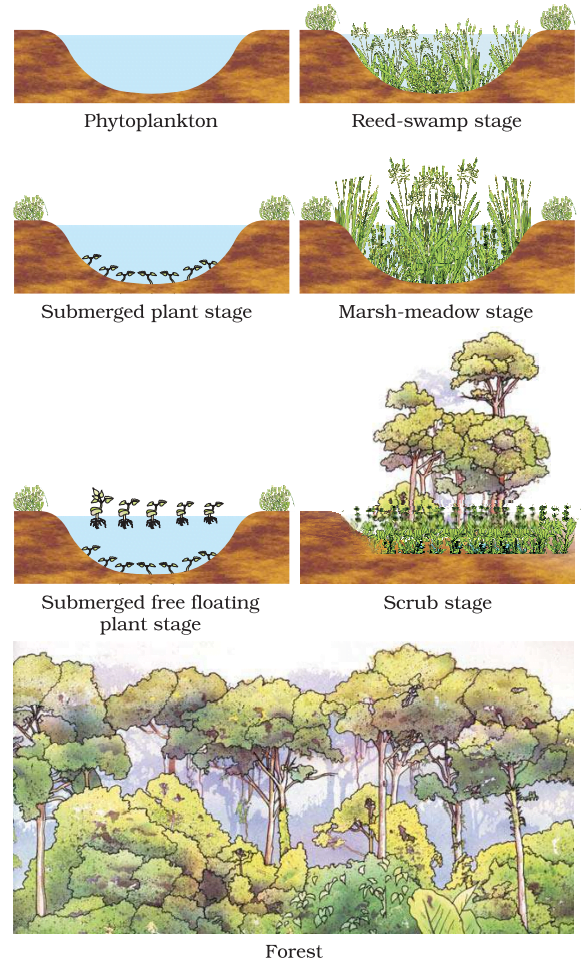
- The sequence of communities of primary succession in water is:
- phytoplankton, sedges, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees.
- phytoplankton, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, sedges, grasses and trees.
- free-floating hydrophytes, sedges, phytoplankton, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees.
- phytoplankton, rooted submerged hydrophytes, floating hydrophytes, reed swamp, sedges, meadow and trees.
- The reservoir for the gaseous type of bio-geochemical cycle exists in
- stratosphere
- atmosphere
- ionosphere
- lithosphere.
- If the carbon atoms fixed by producers already have passed through three species, the trophic level of the last species would be
- scavenger
- tertiary producer
- tertiary consumer
- secondary consumer.
- Which of the following types of ecosystem is expected in an area where evaporation exceeds precipitation, and mean annual rainfall is below 100 mm.
- Grassland
- Shrubby forest
- Desert
- Mangrove.
- The zone at the edge of a lake or ocean which is alternatively exposed to air and immersed in water is called:
- Pelagic zone
- Benthic zone
- Lentic one
- Littoral zone.
- Very Short Question:
- Decomposition is faster if deteritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substance like sugars. When is the decomposition process slower?
- If we count the number of insects on a tree and number of small birds depending on those insects as also the number of larger birds eating the smaller, what kind of pyramid of number would we get?
- Differentiate between Sere and Seral communities.
- Who are generally the pioneer species in a Xerarch succession and in a Hyararch succession?
- Which metabolic process causes a reduction in the Gross Primary Productivity?
- What percentage of photosyntheticallyactive radiation is captured by plants?
- Name the pioners of primary succession in water.
- Name any two man – made ecosystem?
- Define stratification?
- Name the ecological pyramid that is always upright?
- Short Questions:
- What is the shape of pyramid of biomass in sea? Why?
- Give an example of an ecological pyramid which is always upright. Justify your Answer.
- Differentiate between primary succession and secondary succession. Which one occurs faster?
- Gaseous nutrient cycle and sedimentary nutrient cycles have their reservoir. Name them. Why is a reservoir necessary?
- Differentiate between Hydrarch and a Xerarch succession.
- Why is secondary sucession faster than primary sucession?
- Distinguish between upright & inverted pyramids?
- Explain with an example, why is the length of a food chain in an ecosystem generally limited to 3-4 tropic level?
- Long Questions:
- Briefly describe the biotic components of an ecosystem.
- Give an account of factors affecting the rate of decomposition.
- Sometimes due to biotic/abiotic factors, the climax remains in a particular serai stage (pre-climax) without reaching climax. Do you agree with this statement? If yes give a suitable example.
- Assertion & Reason Questions:
- For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Ecosystem is the structural and functional unit of biosphere consisting of abiotic and biotic components which interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature.
Reason: In an ecosystem, energy and matter are continuously exchanged between living and non-living components.
- For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Different ecosystems have different species composition.
Reason: The type of species that can thrive in an ecosystem is dependent upon its geography, topography and climate.
- Case Study Questions:
- Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Except for the deep sea hydro-thermal ecosystem, sun is the only source of energy for all ecosystems on Earth. Of the incident solar radiation less than 50 per cent of it is photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). We know that plants and photosynthetic bacteria (autotrophs), fix Sun’s radiant energy to make food from simple inorganic materials. Plants capture only 2-10 per cent of the PAR and this small amount of energy sustains the entire living world. So, it is very important to know how the solar energy captured by plants flows through different organisms of an ecosystem. All organisms are dependent for their food on producers, either directly or indirectly. The green plant in the ecosystem are called producers. In a terrestrial ecosystem, major producers are herbaceous and woody plants. Likewise, producers in an aquatic ecosystem are various species like phytoplankton, algae and higher plants. You have read about the food chains and webs that exist in nature. Starting from the plants (or producers) food chains or rather webs are formed such that an animal feeds on a plant or on another animal and in turn is food for another. The chain or web is formed because of this interdependency. No energy that is trapped into an organism remains in it for ever. The energy trapped by the producer, hence, is either passed on to a consumer or the organism dies. Death of organism is the beginning of the detritus food chain/web. All animals depend on plants (directly or indirectly) for their food needs.
They are hence called consumers and also heterotrophs. If they feed on the producers, the plants, they are called primary consumers, and if the animals eat other animals which in turn eat the plants (or their produce) they are called secondary consumers. Likewise, you could have tertiary consumers too. Obviously the primary consumers will be herbivores. Some common herbivores are insects, birds and mammals in terrestrial ecosystem and molluscs in aquatic ecosystem.
1) ……………………. Is an herbivore organism in the aquatic ecosystem.
(a) Molluscs
(b) Insects
(c) Mammals
(d) Birds
2) In the ecosystem, green plants are
(a) Consumers
(b) Decomposers
(c) Producers
(d) All of them
3) PAR is a ………………….
(a) Powerful Atomic Radiation.
(b) Photosynthetically Atomic Radiation.
(c) Photosynthetically Active Radiation.
(d) Powerful Active Radiation.
4) Which ecosystem on earth does not require sun as an energy source?
5) Name any two producers from aquatic ecosystem.
- Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
The consumers that feed on these herbivores are carnivores, or more correctly primary carnivores (though secondary consumers). Those animals that depend on the primary carnivores for food are labelled secondary carnivores. A simple grazing food chain (GFC) is depicted below:
| Grass | Goat | Man |
| Producer | Primary consumer | Secondary consumer |
The detritus food chain (DFC) begins with dead organic matter. It is made up of decomposers which are heterotrophic organisms, mainly fungi and bacteria. They meet their energy and nutrient requirements by degrading dead organic matter or detritus. These are also known as saprotrophs (sapro: to decompose). Decomposers secrete digestive enzymes that breakdown dead and waste materials into simple, inorganic materials, which are subsequently absorbed by them. In an aquatic ecosystem, GFC is the major conduit for energy flow. As against this, in a terrestrial ecosystem, a much larger fraction of energy flows through the detritus food chain than through the GFC. Detritus food chain may be connected with the grazing food chain at some levels: some of the organisms of DFC are prey to the GFC animals, and in a natural ecosystem, some animals like cockroaches, crows, etc., are omnivores. These natural interconnection of food chains make it a food web. How would you classify human beings!
1) ……………………….. is a beginning of Detritus food chain.
(a) Living organic matter
(b) Producers
(c) Dead organic matter
(d) Consumers
2) The meaning of sapro word in the saprotrophs is ……………………….
(a) To produce
(b) To divide
(c) To consume
(d) To decompose
3) GFC is a ……………………………..
(a) Global food chain
(b) Grazing food chain
(c) Global food consumers
(d) Grazing form chain
4) Write a short note on Grazing food chain.
5) What is ‘Food web’.
- Answer Key-
- Multiple Choice Answers:
- (b) Marine
- (b) Agaricus
- (b) Tropical rainforests
- (c) Either upright or inverted
- (b) 2-10%
- (a) Tropical rainforest
- (b) 10%
- (a) Orderly and sequential
- (b) equilibrium
- (d) All of the above.
- (b) phytoplankton, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, sedges, grasses and trees.
- (b) atmosphere
- (c) tertiary consumer
- (c) Desert
- (d) Littoral zone.
- Very Short Answers:
- Its slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
- Inverted Pyramid of Number .
- Sere: Entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area.Serial community: Individual transitional community .
- Pioneer species in Hydrarch succession are usually the small phytoplanktons and that in Xerarch succession are usually lichens.
- Respiration.
- 2 – 10%
- Phytoplanktons
- Aquarium & Garden.
- Stratification in an ecosystem refers to the vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels.
- Pyramid of energy.
- Short Answer:
- Inverted, because biomass of fishes far exceeds that of phytoplankton.
- Pyramid of energy is always upright and can never be inverted, because when energy flows from a trophic level to the next trophic level some energy is always lost as heat at each step.
- Primary Succession: Aprocess that starts where no living organisms are there. Secondary succession: Aprocess that starts in areas which have lost all the living organisms that existed there.
- Reservoir for Gaseous nutrient cycle : Atmosphere; for sedimentary nutrient cycle : Earth’s crust. Reservoir is needed to meet with the deficit which occurs due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux.
- HydrarchSuccession: Starts in water proceeds from hydric (aquatic) to mesic (neither dry nor wet) situations. Xerarchsuccession: Starts on barren rock Proceeds from Xeric (dry) conditons.
- Secondary succession refers to community development on sites previously occupied by welldeveloped communities where the environment is both organic & inorganic. Since these bare areaspossesses suitable soil for proper growth so, secondary successes is more rapid them primarysuccession.
- In upright pyramid the number of producers or its biome is maximum in an ecosystem & it decreases progressively at each trophic level. Whereas in inverted pyramid at producer level is minimum & is increasing progressively at each trophic level in a food chain.
- In a food chain at each trophic level about 90% of energy is degraded into heat & only 10% energy is transferred to next tropic level thus of trophic levels in the food chain the amount energy to be transferred to next trophic level will be approximately negligible thus a food chain is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels.
- Long Answer:
- Biotic components: Of an ecosystem’s biotic components, the plants are producers as they introduce food materials and energy into the living world. The animals are consumers because they get food and energy by consuming plants directly thus called primary consumers (herbivores); secondary/ tertiary consumers (carnivores) obtain energy and food indirectly from plants, and microorganisms are decomposers for they flourish by breaking dead organic matter to simple substances that are returned to environment for reuse by plants.
In an ecosystem, nutrients are used again and again in a cyclic manner, whereas energy trapped from sunlight is lost as heat.
- Factors affecting decomposition:
- The upper layer of soil is the main site of decomposition processes in the ecosystem.
- The rate of decomposition of detritus is affected by climatic factors and the chemical quality of detritus.
- Temperature and soil moisture affect the activities of root microbes.
- The chemical quality of detritus is determined by the relative proportion of water-soluble substances, polyphenols, lignin, and nitrogen.
- Sometimes pre-climax stage remains in a particular serai stage without reaching the climax because during ecological succession any change in abiotic and biotic components may affect the particular serai stage, leading to the pre-climax stage before the climax is achieved.
This type of condition occurs in the presence of seeds and other propagules. This secondarily based area may be invaded by moss or exotic weeds thus exhibiting succession seriously and the climax community is never regenerated.
- Assertion and Reason Answers:
1) a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Ecosystems include living organisms, the dead organic matter produced by them, the abiotic environment within which the organisms live and exchange elements and the interactions between these components. Ecosystems include the concept that living organisms continually interact with each other and with the environment to produce complex systems with emergent properties, such that “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts” and “everything is connected”. The idea of the ecosystem relates to the idea that all organisms in the environment are engaged in relationships with every other aspect (like resources and other organisms) in that environment. Ecosystems deal with energy and nutrient flow through a system/community.
2) a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
A Each ecosystem has different kinds of species. This is because the type of species that can thrive in an ecosystem is dependent upon its geography, topography and climate. For example, the desert biomes have species that are well adapted to life in the sand with limited access to water, such as camels and cacti. The species in tundras have adaptations to keep the body warm, such as the polar bear that has fur and fat layers under its skin.
- Case Study:
- (a) Molluscs.
- (c) Producers.
- (c) Photosynthetically Active Radiation.
- The deep sea hydro-thermal ecosystem is the ecosystem on earth that does not require sun as an energy source.
- Algae and phytoplankton both are producers in an aquatic ecosystem.
- (c) Dead organic matter.
- (d) To decompose.
- (b) Grazing food chain.
- The producers are present in beginning of grazing food chain. Grass is taken as producer in this chain. Then goat is primary consumer because it eats or consume grass. Man are secondary consumers in the chain because man consume goat which consumes grass.
- The normal interconnection of food chain is known as Food web.
Class 12 Biology All Chapter Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Question Answer
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Notes
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question Answer
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes Question Answer
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Notes
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Question Answer
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Notes
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question Answer
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Notes
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question Answer
- Chapter 7 Evolution Notes
- Chapter 7 Evolution Question Answer
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Notes
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Question Answer
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Notes
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Question Answer
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Notes
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Question Answer
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Notes
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Question Answer
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Notes
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Question Answer
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Notes
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Question Answer
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Notes
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Question Answer
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Notes
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Question Answer
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Notes
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Question Answer