Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Question Answer: Explore comprehensive question-answer solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 on Organisms and Populations. Prepare for exams with detailed explanations, examples, and key insights covering topics such as population interactions, ecological adaptations, population growth, and ecosystem dynamics to deepen your understanding of organisms and their interactions in natural environments.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Question Answer
- Multiple Choice Questions:
- Autecology is the
- relation of a population to its environment
- relation of an individual to its environment
- relation of a community to its environment
- relation of a biome to its environment.
- Ecotone is:
- A polluted area
- The bottom of a lake
- A zone of transition between two communities
- A zone of developing community.
- Biosphere is:
- A component in the ecosystem
- Composed of the plants present in the soil
- Life in the outer space
- Composed of all living organisms present on the earth which interact with the physical environment.
- Ecological niche is:
- the surface area of the ocean
- a an ecologically adapted zone
- the physical position and functional role of a species within the community
- formed of all plants and animals living at the bottom of a lake.
- According to Allen’s Rule, the mammals from colder climates have:
- shorter ears and longer limbs
- longer ears and shorter limbs
- longer ears and longer limbs
- shorter ears and shorter limbs.
- Salt concentration (salinity) of the sea measured in parts per thousand is:
- 10-15
- 30-70
- 0-5
- 30-35.
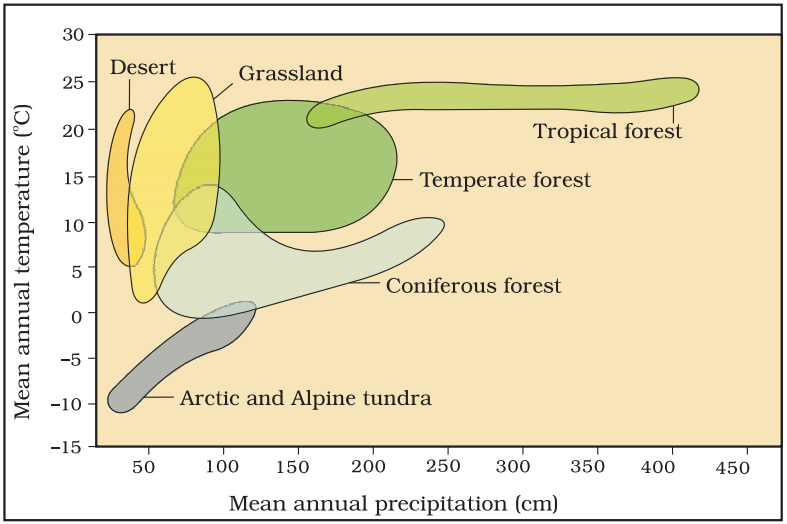
- Formation of tropical forests needs mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation as:
- 18-25°C and 150-400 cm
- 5-15°C and 50-100 cm
- 30-50°C and 100-150 cm
- 5-15°C and 100-200 cm.
- Which of the following forest plants controls the light conditions at the ground?
- Lianas and climbers
- Shrubs
- Tall trees
- Herbs.
- What will happen to a well growing herbaceous plant in the forest if it is transplanted outside the forest in a park?
- It will grow normally
- It will grow well because it is planted in the same locality
- It may not survive because of change in its microclimate
- It grows very well because the plant gets more sunlight.
- If a population of 50 paramecia present in a pool increases to 150 after an hour, what would be the growth rate of population?
- 50 per hour
- 200 per hour
- 5 per hour
- 100 per hour.
- What would be the per cent growth or birth rate per individual per hour for the same population mentioned in the previous question?
- 100
- 200
- 50
- 150.
- A population has more young individuals compared to the older individuals. What would be the status of the population after some years?
- It will decline.
- It will stabilize.
- It will increase.
- It will first decline and then stabilize.
- What parameters are used for tiger census in our country’s national parks and sanctuaries?
- Pugmarks only
- Pug marks and faecal pellets
- Faecal pellets only
- Actual head counts.
- Which of the following would necessarily decrease the density of a population in a given habitat?
- Natality > mortality
- Immigration > emigration
- Mortality and emigration
- Natality and immigration.
- A protozoan reproduces by binary fission. What will be the number of protozoans in its population after six generations?
- 128
- 24
- 64
- 32.
- Very Short Question:
- Which are the factor responsible for the wide variety of habitat formed within each biome?
- Fresh water animals are unable to survive for long in sea water. Give reason.
- With which population growth model is the Verhulst Pearl equation associated?
- Define diapause. Which organisms exhibit it?
- Calculate the death rate if 6 individuals in a laboratory population of 60 fruit flies died during a particular week.
- In biological control method, one living organism is used against another to check its uncontrolled growth. Which kind of population interaction is involved in this?
- Write what do phytophagous insects feed on?
- Why do leaves contains Sunken stomata?
- Name the type of interaction that is detrimental to both the interaction.
- What type of interaction is shown by sparrows eating the seeds?
- Short Questions:
- What are the four levels of biological organisation with which ecology basically deals?
- Differentiate between stenohaline and euryhaline organisms.
- List four features which enable the Xeric plants to survive in the desert conditions.
- Mention the attributes which a population has but not an individual organism.
- Differentiate between stenothermal and eurythermal organisms.
- What are the four ways through which the living organisms respond to abiotic factors?
- Why do clown fish and sea anemone pair up? What is this relationship called?
- Distinguish between ectotherms& Endotherms?
- Long Questions:
- Explain the ecological hierarchy.
- Why do all the freshwater organisms have contractile vacuoles whereas the majority of marine organisms lack them?
- Discuss life-history traits of an organism that have evolved in relation to the constraints imposed by biotic and abiotic factors in their habitat.
- Assertion & Reason Questions
- For question two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Mycorrhizal relation exists between Boletus and Pinus.
Reason: It is a symbiotic interaction.
- For question two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Amensalism is a negative interaction between two living individuals.
Reason: In amensalism, allochemics are secreted by one individual.
- Case Study Questions:
1. Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Ananya is a biologist, her research guide assigned project, i.e., to determine the effect ofin tra-specific competition on the growth of sapling of Eucalyptus. For this, she designed an experiment in which two sets of pots were used. ln the first set (set A) only I sapling was planted per pot and in the other set (set B) 16 saplings were planted per pot. To check for the effect of intra-specific competition on allocation of resources, a decreasing amount of water was added to each set. The results have been graphically indicated. Which of the following conclusions can indicated as follows:

- Which of the following statements can be concluded from the given study?
- More resources are allocated to the root during low water conditions.
- Competition for water among individuals of a population causes more root growth as compared to individuals who are growing alone.
- Lesser leaves are formed under low water conditions.
- Root growth is higher in individual grown singly as compared to individuals in populations.
- Which of the following associations is an example of competitions?
- Cuscuta and hedge plant.
- Balanus and Cathamalus.
- Cactus and moth.
- Orchid and mango.
- If ‘+’ sign is assigned to beneficial interaction, ‘-‘ sign to detrimental and O sign to neutral interaction, then the population interaction of competition refers to:
- +, +
- -, –
- +, –
- +, 0
- lntraspecific competition is more severe due to:
- similar needs.
- similar adaptations.
- common resources.
- all of these.
- Assertion: Two members of a competing species may co-exist.
Reason: Different individuals of a species have different resource requirements.
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
2. Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Age sex structure of a population can be depicted in the form of a pyramid by plotting the percentage of population of each sex in each age class. Two age sex pyramids are as follows.

- Which of the following is correct regarding pyramid B?
- It represents stable population.
- It represents expanding population.
- It represents declining population.
- Both (a) and (b).
- Total number of individuals of a species per unit area per unit time is called.
- Population size.
- Population density.
- Demography.
- Population dynamics.
- Which of the following is correct regarding age sex pyramid A and B?
- A represents the age sex pyramid of developed country.
- B represents the age sex pyramid of developing country.
- A represents rapidly growing population.
- Both (a) and (b).
- A population with a large proportion of older individuals than younger ones will likely to:
- Grow larger first and then decline.
- Continue to grow indefinitely.
- Decline.
- None of these.
- Assertion: Bell shaped age pyramid represents a stable population.
Reason: ln a stable population, proportion of individuals in reproductive age group is higher than the individuals in pre reproductive age group.
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
- Answer Key-
- Multiple Choice Answers:
- (b) relation of an individual to its environment
- (c) A zone of transition between two communities
- (d) Composed of all living organisms present on the earth which interact with the physical environment.
- (c) the physical position and functional role of a species within the community
- (d) shorter ears and shorter limbs.
- (d) 30-35.
- (a) 18-25°C and 150-400 cm
- (c) Tall trees
- (c) It may not survive because of change in its microclimate
- (d) 100 per hour.
- (b) 200
- (c) It will increase.
- (b) Pug marks and faecal pellets
- (c) Mortality and emigration
- (c) 64
- Very Short Answers:
- Regional and local variations
- Due to osmotic problems.
- Logistic Growth.
- A stage of suspended development, zooplanktons.
- 6/60 =0.1 individuals per fruitfly per week.
- Predation.
- Plant sap and other parts of plant.
- Leaves contains sunken stomata i.e. Stomata arranged in deep pits to minimizes water loss by transpiration.
- Competition.
- Predation.
- Short Answer:
- Organisms, population, communities and biomes.
- Euryhaline: Organisms tolerant in wide range of salinities.
Stenohaline: Organisms tolerant to narrow range of salinities.
(i) thick cuticle
(ii) Stomata in deep pits
(iii) Stomata closed during day time
(iv) leaves reduced to spines (CAM photosynthetic pathway).
- Birth rate, Death rate, Sex ratio, age groups.
- Eurythermal: Organisms that can tolerate and thrive in wide range of temperatures Stenothermal: Organisms restricted to a narrow range of temperature.
- (i) Regulate (ii) Conform (iii) migrate (iv) Suspend
- Clown fish lives in tentacles of sea Anemone and gets protection from predators.
Interaction – commensalism.
- Ectotherms are those animals whose body temperature changes & matches with that of environment in which they are living whereas Endotherms are those animal whose body temperature is maintained relatively constant by physiological regulation.
- Long Answer:
- Ecological hierarchy: It is a series of graded ecological categories.
Characteristics of ecological hierarchy:
- A biological unit at each level has a specific structure and function.
- In this hierarchy, smaller biological units coordinate to form the next higher level of organization.
- Only the organisms show free existence.
- Organisms cannot live in isolation.
- At each level, different units show interdependence.
- At each level, the unit shows interaction with the physical environment (energy and matter).
- The biological units are successfully adapted to their environment.
- Contractile vacuole helps in maintaining salt and water level called osmoregulation. Because of the cellular environment of a freshwater organism such as Amoeba, Paramecium etc. being hypertonic, the water diffuses inside the cell constantly and gets collected in the contractile vacuole, which squeezes the extra water out of the cell periodically.
While in the case of marine protozoan’s organisms, this does not occur due to high salt concentration. These organisms live in isotonic conditions in seawater. Thus, there is no need for contractile vacuole.
- According to ecologists, life-history traits of an organism have evolved in relation to the constraints imposed by the biotic and abiotic factors in their habitats.
- It can be illustrated with vast variations and life history.
- The evolution of populations aims at improving reproductive fitness or Darwinian fitness to the maximum in their habitats.
- They evolve towards the most efficient reproductive strategy.
- Organisms like Pacific Salmon fish and bamboo breed only once in their lifetime.
- Most birds and mammals breed many times during their lifetime.
- Oysters and pelagic fishes produce a large number of small-sized offspring.
- Birds and mammals produce a small number of large-sized offspring.
- Assertion & Reason Answers
- (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Mycorrhiza is a mutualistic or symbiotic interaction in which a fungus (e.g. Boletus) and a root of plant ( e.g. Pinus) are involved. The root provides food and shelter to the fungus. The fungus helps the plant in solubilization and absorption of minerals, water uptake and protection against pathogenic fungi.
- (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Amensalism is an interaction between two living individuals of different species in which an organism does not allow other organism to grow or live near it. Inhibition is achieved through the secretion of chemicals called allochemics.
- Case Study Answers:
1.
- (b) Competition for water among individuals of a population causes more root growth as compared to individuals who are growing alone.
Explanation:
Competition is a sort of rivalry among two or more organisms for obtaining the same resources. The competition among individuals of the same species is called intraspecific competition and among members of different species is called interspecific competition. lntraspecific competition is more severe than interspecific competition due to similar needs. Now, according to the given graph, competition for water in a population leads to more root weight (mg) per leaf area (cm2). This is because competition causes more root growth so that each sapling can derive more water from the pot.
- (b) Balanus and Cathamalus.
Explanation:
The association or interactions of Cuscuta and hedge plant is parasitism, cactus and moth is predation and orchid and mango is commensalism.
- (b) -, –
- (d) all of these.
Explanation:
lntraspecific competition is more severe because of common resource, similar needs and similar adaptations.
- (d) Both assertion and reason are false.
2.
- (b) It represents expanding population.
- (b) Population density
Explanation:
Population density is the number of individual present per unit area at a given time.
- (d) Both (a) and (b).
Explanation:
A represents nearly stable population whereas B represents rapidly growing population.
- (c) Decline.
Explanation:
A population with large number of older individuals than younger ones is likely to decline since older individuals do not take part in reproduction.
- (C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
Explanation:
In a bell-shaped age pyramid, die number of pre-reproductive and reproductive individuals is almost equal. Post-reproductive individuals are comparatively fewer. It represents a stable population.
Class 12 Biology All Chapter Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Question Answer
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Notes
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question Answer
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes Question Answer
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Notes
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Question Answer
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Notes
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question Answer
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Notes
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question Answer
- Chapter 7 Evolution Notes
- Chapter 7 Evolution Question Answer
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Notes
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Question Answer
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Notes
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Question Answer
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Notes
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Question Answer
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Notes
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Question Answer
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Notes
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Question Answer
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Notes
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Question Answer
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Notes
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Question Answer
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Notes
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Question Answer
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Notes
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Question Answer