Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Question Answer: Find comprehensive question-answer solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 on Reproduction in Organisms. Get ready for exams with detailed explanations, examples, and key insights to master the topic effectively.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Question Answer
- Multiple Choice Questions:
- A few statements describing certain features of reproduction are given below:
- Gametic fusion takes place
- Transfer of genetic material takes place
- Reduction division takes place
- Progeny have some resemblance with parents
Select the options that are true for both asexual and sexual reproduction from the options given below:
- i and iii
- ii and iii
- ii and iv
- i and iii
- The term ‘clone’ cannot be applied to offspring formed by sexual reproduction because:
- Offspring do not possess exact copies of parental DNA.
- DNA of only one parent is copied and passed on to the offspring.
- Offspring are formed at different times
- DNA of parent and DNA of offspring are completely different.
- Amoeba and Yeast reproduce asexually by fission and budding respectively, because they are:
- Microscopic organisms
- Heterotrophic organisms
- Unicellular organisms
- Uninucleate organisms.
- A few statements with regard to sexual reproduction are given below:
- Sexual reproduction does not always require two individuals.
- Sexual reproduction generally involves gametic fusion.
- Meiosis never occurs during sexual reproduction
- External fertilisation is a rule during sexual reproduction.
Choose the correct statements from the options below:
- i and iv
- i and ii
- ii and iii
- i and iv
- A multicellular, filamentous alga exhibits a type of sexual life cycle in which the meiotic division occurs after the formation of zygote. The adult filament of this alga has
- Haploid vegetative cells and diploid gametangia
- Diploid vegetative cells and diploid gametangia
- Diploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia
- Haploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia.
- The male gametes of rice plant have 12 chromosomes in their nucleus. The chromosome number in the female gamete, zygote and the cells of the seedling will be respectively
- 12, 24, 12
- 24, 12, 12
- 12, 24, 24
- 24, 12, 24
- Given below are a few statements related to external fertilisation. Choose the correct statements.
- The male and female gametes are formed and released simultaneously.
- Only a few gametes are released into the medium.
- Water is the medium in a majority of organisms exhibiting external fertilisation.
- Offspring formed as a result of external fertilisation have better chance of survival than those formed inside an organism.
- iii and iv
- i and iii
- ii and iv
- i and iv
- The statements given below describe certain features that are observed in the pistil of flowers.
- Pistil may have many carpels
- Each carpel may have more than one ovule
- Each carpel has only one ovule
- Pistil has only one carprel
Choose the statements that are true from the options below:
- i and ii
- i and iii
- ii and iv
- iii and iv
- Which of the following situations correctly describe the similarity between an angiosperm egg and a human egg?
- Eggs of both are formed only once in a lifetime
- Both the angiosperm egg and human egg are stationary
- Both the angiosperm egg and human egg are motile.
- Syngamy in both results in the formation of zygote
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- ii and iv
- iv only
- iii and iv
- i and iv
- Appearance of vegetative propagules from the nodes of plants such as surgarcane and ginger is mainly because:
- Nodes are shorter than internodes
- Nodes have meristematic cells
- Nodes are located near the soil
- Nodes have non-photosynthetic cells
- Which of the following statements supports the view that elaborate sexual reproductive process appeared much later in the organic evolution?
- Lower groups of organisms have simpler body design
- Asexual reproduction is common in lower groups
- Asexual reproduction is common in higher groups of organisms
- There is high incidence of sexual reproduction in angiosperms and vertebrates.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- i and ii
- i and iii
- ii and iv
- ii and iii
- Offspring formed by sexual reproduction exhibit more variations than those formed by asexual reproduction because:
- Sexual reproduction is a lengthy process
- Gametes of parents have qualitatively different genetic composition
- Genetic material comes from parents of two different species
- Greater amount of DNA is involved in sexual reproduction.
- Choose the correct statement from amongst the following:
- Dioecious (hermaphrodite) organisms are seen only in animals
- Dioecious organisms are seen only in plants
- Dioecious organisms are seen in both plants and animals
- Dioecious organisms are seen only in vertebrates.
- There is no natural death in single celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria because:
- They cannot reproduce sexually
- They reproduce by binary fission
- Parental body is distributed among the offspring
- They are microscopic.
- There are various types of reproduction. The type of reproduction adopted by an organism depends on:
- The habitat and morphology of the organism
- Morphology of the organism
- Morphology and physiology of the organisms
- The organism’s habitat, physiology and genetic makeup
- Very Short Question:
- Offsprings produced by asexual reproduction are referred to as clones. Why?
- Name the most invasive aquatic plant weed which is called as Terror of Bengal.
- How does Zygote usually differ from Zoospore in terms of ploidy?
- Mention the main difference between the offspring produced by asexual reproduction and progeny produced by sexual reproduction.
- Which characteristic property of Bryophyllum is exploited by gardeners and farmers?
- What represents the life span of an organism?
- Which individuals can be termed as clones?
- How do the following organisms reproduce: Paramoecium and Penicillium?
- State the function of a vegetative propagule.
- How will you grow a banana and a ginger plant?
- Short Questions:
- Higher organism have resorted to sexual reproduction inspite of its complexity. Why?
- Tapeworms posses both male and female reproductive organs. What is the name given to such organism? Give two more examples of such organisms.
- Study the relationship between first two words and suggest a suitable word for fourth place.
- Male flower: Stamens :: Female Flower : ………………………..
- Birds: oviparous :: Primates : ………………………..
- Chlamydomonas : Zoospores :: Penicilium : ………………………..
- Ginger: Rhizome :: Agave : ………………………..
- Bryophytes and Pteridophytes produce a large number of male gametes but relatively very few female gametes. Why?
- Enlist the significance of reproduction.
- Why do hilly areas of Kerela, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu transform into blue stretches that attracts many tourists?
- Define ‘oestrus’ and ‘menstrual’ cycles.
- What regulates the reproduction processes and the associated behavioural expressions in organisms?
- Long Questions:
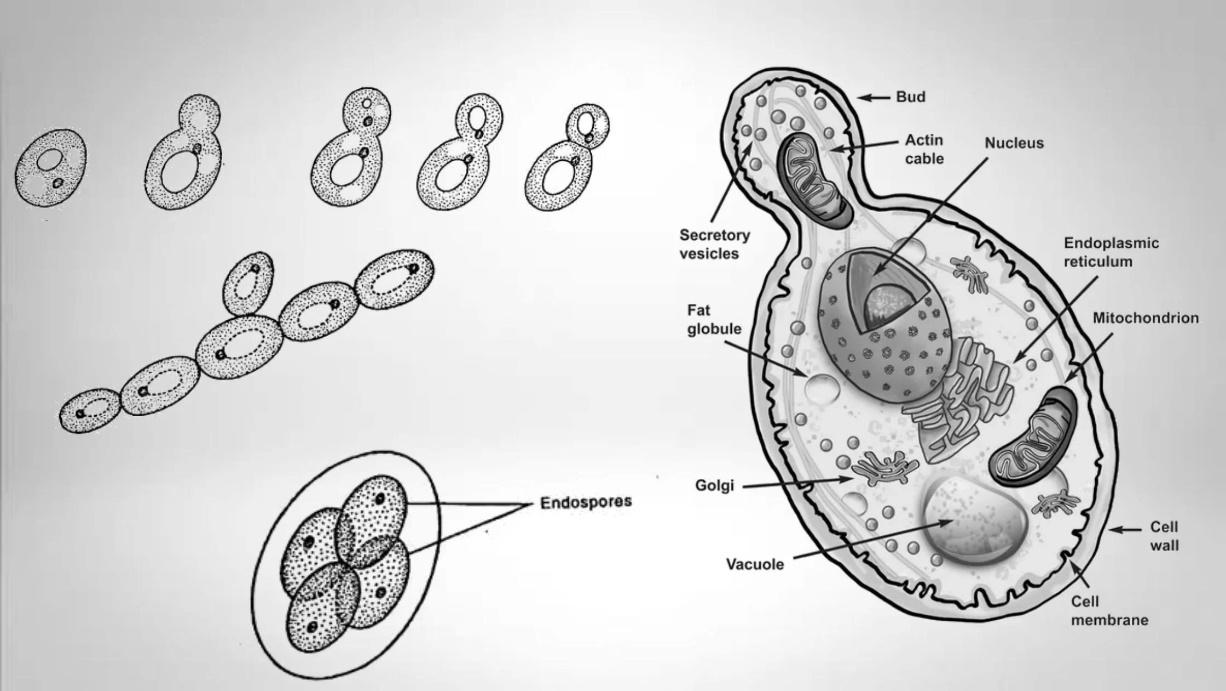
- Explain the process of budding in yeast.
- Describe the importance of vegetative propagation.
- Describe the post-fertilisation changes in a flower.
- Assertion & Reason Questions:
- For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Asexual reproduction involves formation of clones of an organism.
Reason: Clones are morphologically and genetically similar individuals.
- For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Several seed bearing plants propagate vegetatively.
Reason: Sweet potatoes undergo vegetative propagation by means of root tubers.
- Answer Key-
- Multiple Choice Answers:
- (c) ii and iv
- (a) Offspring do not possess exact copies of parental DNA.
- (c) Unicellular organisms
- (b) i and ii
- (d) Haploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia.
- (c) 12, 24, 24
- (b) i and iii
- (a) i and ii
- (b) iv only
- (b) Nodes have meristematic cells
- (c) ii and iv
- (b) Gametes of parents have qualitatively different genetic composition
- (c) Dioecious organisms are seen in both plants and animals
- (c) Parental body is distributed among the offspring
- (d) The organism’s habitat, physiology and genetic makeup
- Very Short Answers:
- Because offsprings produced by Asexual reproduction is morphologically and genetically identical to parent.
- Water hyacinth (Eicchornia)
- Zygote diploid, zoospore haploid.
- Offspring produced by asexual reproduction are genetically similar while progeny produced by sexual reproduction exhibit genetic variation.
- Adventitious bud arising from margin of the leaf.
- The period from the birth to the natural death of an organism represents its life span.
- The individuals who are morphologically and genetically identical are called clones.
- a) Paramoecium reproduces by the process of binary fission.
b) Penicillium reproduces with the help of asexual structures called conidia.
- The vegetative propagules are the asexual vegetative structures of the plant that are capable of giving rise to a new plant.
- The rhizomes of a banana and a ginger are used to propagate new plantlets.
- Short Answer:
- Because of variations, gene pool, Vigour and Vitality and Parental care.
- Hermaphrodite; Examples : Earthworm, Leech.
- (a) Carpel (b) Viviparous
(c) Conidia (d) Bulbil
- Because male gemete need medium (water) to reach egg/female gamete.A large number of the male gametes fail to reach the female gamete.
- Significance of reproduction includes:
- Propagation of species.
- Sustenance of life on this planet.
- Variation introduced during reproduction plays a role in evolution of new species.
- Strobilanthus kunthiana which flowers only once in every 12 years flowered in 2006 that resulted into transformation of the hilly tracks of Kerela, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu into blue stretches.
- Non- Primates like cows, sheep etc. show certain cyclic changes during reproduction called oestrus cycle while Primates like apes, humans the cycle is referred to as menstrual cycle.
- Interaction between hormones and certain environmental factors regulate the reproductive processes and the associated behavioural expressions of organisms.
- Long Answer:
- Budding in yeast. It is a common type of vegetative reproduction. In a medium which is abundantly supplied with sugar, yeast cytoplasm forms a bud-like outgrowth. The growth soon enlarges and a part of the nucleus protrudes into the bud and breaks off. The bud then begins to grow and then separates from the mother cell. Often it will itself form a bud before it breaks away, and straight or branched chains are produced.

Thus, as a result, branched or unbranched chains of cells called pseudo my cilium are produced. The cells are loosely held together. Sooner or later they become independent.
- Merits of vegetative propagation:
- Plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically similar and constitute a uniform population called a clone.
- Plants with reduced power of sexual reproduction, long dormant period of seed, poor viability, etc. are multiplied by vegetative methods.
- Some fruit trees like banana and pineapple do not produce viable seeds. So these are propagated by only vegetative methods.
- It is a more rapid and easier method of propagation.
- Good characters are preserved by vegetative propagation.
- Some plants such as doob grass (Cynodon dactylon) which produce only a small quantity of seed are mostly propagated by vegetative propagation.
- Grafting helps in getting an economically important plant having useful characteristics of two different individuals in a short time.
- Post-fertilisation changes in a flower.

- Assertion and Reason Answers:
1) b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
The reproduction is known as asexual reproduction, when an offspring is produced by a single parent without the involvement of gamete formation. As a result, the offspring that are produced are not only similar to one another but are also exact copies of their parent. Such a group of morphologically and genetically similar individuals are called clones.
2) b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Formation of new plants by means of vegetative units as tubers, buds, rhizomes is called vegetative propagation. It is useful for producing large number of offsprings within a short time and for preserving qualities such as disease resistance. In sweet potato, root tubers take part in vegetative propagation.
Class 12 Biology All Chapter Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Notes
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms Question Answer
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Notes
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question Answer
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes
- Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Notes Question Answer
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Notes
- Chapter 4 Reproductive Health Question Answer
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Notes
- Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question Answer
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Notes
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question Answer
- Chapter 7 Evolution Notes
- Chapter 7 Evolution Question Answer
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Notes
- Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Question Answer
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Notes
- Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production Question Answer
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Notes
- Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare Question Answer
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Notes
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principal and Processes Question Answer
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Notes
- Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Question Answer
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Notes
- Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Question Answer
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Notes
- Chapter 14 Ecosystem Question Answer
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Notes
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity And Conservation Question Answer
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Notes
- Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Question Answer