Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell The Unit Of Life Notes and Question Answer: Very well-prepared notes for chapter 8 “Cell The Unit Of Life” by subject experts will help you in all types of exams. Along with this, where important questions and their answers and question bank have been given, which you can prepare according to your exam.
Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell The Unit Of Life Notes
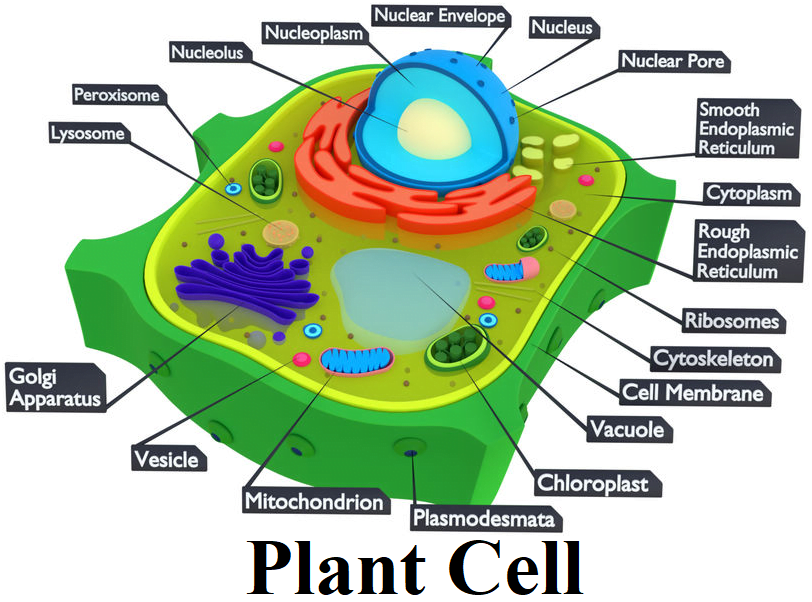
Cell: A cell is defined as the most basic, structural and functional unit of all living organisms. Essentially, a cell is a structure that contains organelles which provide necessary functions to sustain itself. However, not all cells are the same.

Prokaryotic cells
- Membrane-bound nucleus is absent.
- Cells are smaller in size.
- Single chromosome is present.
- Membrane-bound organelles are absent.
Eukaryotic cells
- Membrane-bound nucleus is present.
- Cells are larger in size.
- More than one chromosome is present.
- Membrane-bound organelles are present.
Animal cell
- Cell membrane is composed of lipids that are arranged in bilayer. The lipid component is mainly composed of phosphoglycerides. Later it was found that protein is also present in cell membrane. Ratio of protein and lipids varies in different cells.
- Membrane protein may be integral or peripheral. Integral protein remains buried in membrane but peripheral protein lies on the surface.
- Singer and Nicholson (1972) proposed fluid mosaic model. According to this model, the quasi-fluid nature of lipid enables lateral movement of protein within the bilayer of lipids.

Eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotic cells Possess an organized nucleus with nuclear envelope and have a variety of complex locomotory and cytoskeletal structures.
Active Transport
The transport involves an expenditure of energy by the cells, It occurs against the concentration gradient. It is a rapid process.
Passive Transport
The cells do not spend energy in passive transport, this transport is always along the concentration gradient. It is comparatively slow process.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum are the tubular structure scattered in the cytoplasm. Rough endoplasmic reticulum bears ribosomes on its surface. RER is involved in protein synthesis and secretion. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not bear ribosomes on its surface. SER is involved in lipid synthesis and steroidal hormones.

Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus was first observed by Camillo Golgi in 1898 near nucleus. They consist of many flat, disc-shaped sacs or cisternae stacked parallel to each other. Golgi apparatus performs the function of packaging of materials and its transportation. A number of protein synthesized by ribosomes are modified in cisternae of Golgi apparatus. Golgi apparatus is the site for synthesis of Glycoproteins and glycolipids.

Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicular structures formed by the process of packaging in the Golgi apparatus. They are rich in hydrolytic enzymes- lipase, protease, carbohydrates active at acidic PH. These enzymes are capable of digesting carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.

Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound space found in cytoplasm containing water, sap and excretory product. They are bound by single membrane. They form contractile vacuole and food vacuole in many organisms.

Mitochondria
Mitochondria is double membrane-bound structure with the outer membrane and inner membrane dividing its lumen in two compartments. The inner membrane forms a number of infoldings called cristae towards the matrix.

Plastids
Plastids are found in plant cells and in Euglenoids.
Plastids are three types:
Chloroplast (Contain chlorophyll and caratenoids).
Chromoplast (Contain carotene and xanthophyll).
Leucoplast (Colorless plastids).
- Chloroplast: Contains chlorophyll pigment and carotenoids and performs photosynthesis
- Chromoplast: Contains carotene and xanthophylls. They impart a specific color to flowers and fruits and help in pollination and dispersal of seeds
- Leucoplast: They are colorless and store various food products, e.g., amyloplasts- store starch, proteinoplasts or aleuroplasts- store proteins, elaioplasts- store fat.

Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell The Unit Of Life Mind Map

Important Questions
- Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1. Ribosomes were discovered by
(a) Golgi
(b) Porter
(c) Robertis
(d) Palade
Question 2. In which component of a mitochondrion ATP is synthesied?
(a) Matrix
(b) outer membrane
(c) crista
(d) F0-F1 complex (Oxysome)
Question 3. Tonoplast, a differentially permeable membrane, surround the
(a) nucleus
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Vacuole
Question 4. Addition of the new cell wall material in the existing one is
(a) Deposition
(b) Aggregation
(c) Intussusception
(d) apposition
Question 5. The interphase nucleus is enclosed in
(a) a porous double membrane
(b) a non-porous single membrane
(c) a porous double membrane
(d) many membranes
Question 6. The chloroplast thylakoids are in the form of
(a) interconnected sacs
(b) independent discs
(c) interconnected tabules
(d) stalked discs.
Question 7. Aerobic respiration is performed by
(a) glyoxisome
(b) lysosomes
(c) mitochondria
(d) stalked discs.
Question 8. Plant cell differ from animal cell in having
(a) mitochondria
(b) cell wall
(c) golgi bodies
(d) ribosomes
Question 9. The cell wall of certain fungi is made of
(a) lignin
(b) pectin
(c) suberin
(d) chitin
Question 10. Desmosomes are connected with
(a) cytolysis
(b) cell division
(c) cell excretion
(d) cell adherence.
Question 11. Fluid mosaic model of cell membrane state that it has lipid bilayer with
(a) proteins on the outer surface only.
(b) Some proteins embedded and some on the surface.
(c) Proteins on both the surfaces.
(d) Proteins embedded and some on the surface.
Question 12. Fluid mosaic model of cell membrane was proposed by
(a) Singer and Nicholson
(b) waston and crick
(c) Robertson
(d) danielli and davson
Question 13. Ribosomes are centres
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) liquid synthesis
(c) Respiration
(d) protein synthesis
Question 14. A membrahe covering
(a) Mitochondrion
(b) nucleolus
(c) Plastid
(d) Lysosome
Question 15. Solar energy is converted into ATP/chemical energy by
(a) Chloroplast
(b) Ribosome
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Peroxisome
- Fill In the Blanks:
- All organisms are composed of ………….. Some are composed of a single cell and called …………… organisms while others, like us, are composed of many cells and called …………… organisms.
- The study of structure, composition, functions and life processes of the cell is called ……………
- ……………… was the first person to describe the cell in 1865 when he used a microscope built by him to examine a thin slice of cork
- In 1831, …………….. made on important discovery when he reporeted the presence of a small sphere in the cells of the orchid root
- ………….. and ………….. combined their views and formulated the cell theory
- The presence of several types of organ systems in the body of multicellular organism is a unique example of …………….
- True or False:
- Sometimes a few chromosomes have secondary constrictions at a constant location, which are their non-staining region and give the appearance of a small fragment called the satellite.
- Every chromosome essentially has a primary constriction or the centromere on the sides of which disc shaped structures called kine- tochore, for the attachment of the spindle fibres, is also present.
- The biochemical analysis of the isolated chromatin has revealed that it contains DNA, some basic protein called histones, some nonhistone proteins and also RNA.
- The electron microscope has revealed that the nuclear envelope, which consists of two parallel membranes spaced by 10 to 50nm called the perinuclear space.
- The eukaryotic cells usually possess a large sized, almost centrally located and densely stained organelle containing the genetic material called nucleus.
- The central part of the centriole is also proteinaceous called the hub, which is connected with a tubules of the peripheral tripets by radial spokes made up of protein.
- Very Short Question:
- Who gave the term chromosome?
- Define a cell coat.
- Where is dynein present?
- Define sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- What are pili?
- What are fimbriae?
- Name the organelle of the cell called ‘Suicidal-bag’?
- Define cytoplasm.
- Define plasmodesmata.
- What are the three parts of a flagellum?
- Short Questions:
- Give the fundamental similarities in all cells:
- What are Cytoskeletal Structures?
- What are the main functions of the cell wall?
- List the functions of Golgi bodies.
- Name different types of the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Why does the efficiency of a cell decrease with an increase in size in a unicellular organism?
- The cell is “an open dynamic system” discuss.
- On what basis can we consider the cell as an autonomous unit?
- Long Questions:
- What is the role of the plasma membrane in the compartmentalization of the cell?
- The cells of unicellular organisms are usually spherical whereas those of multicellular tend to be many-sided. Why?
- Discuss how the method of science is reflected in the formulation t of cell theory?
- If, as the second law of thermodynamics states, “the free energy in any system tends to decrease”, how is it that the earth maintains so many living organisms, each in a highly organized, high free energy state?
- Explain the structure and function of mitochondria.
Assertion Reason Question-
- In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Assertion: Organisms are made up of cells.
Reason: Cells are structural unit of living organisms. A cell keeps its chemical composition steady within its boundary.
- In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Assertion: Specialization of cells is useful for organism.
Reason: It increases the operational efficiency of an organism.
Case Study Based Question-
- Observe the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow

(i) Identify the labels A, B and C shown in the above diagram.
(ii) The label ‘C’ in the given diagram is the site of
(a) respiration
(b) photosynthesis
(c) protein synthesis
(d) fat synthesis
(iii) Difference between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum is that
(a) rough ER has ribosomes
(b) smooth ER has ribosomes
(c) smooth ER takes part in protein synthesis
(d) Both has F1 particles
(iv) Ribosomes are
I. Non-membrane bound.
II. Absent in plastids and mitochondria.
III. Present in the cytoplasm and RER.
Choose the correct option.
(a) Only II
(b) I and II
(c) I, II and III
(d) I and III
(v) Which of the following statements are true about endoplasmic reticulum?
I. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) makes lipids.
II. It is also called the control centre of the cell.
III. It processes carbohydrates.
IV. It modifies chemicals that are toxic to the cell.
Choose the correct option
(a) I, II and III
(b) I, III and IV
(c) I and IV
(d) All of these
- Observe the diagram shown below and answer the following questions.

(i) Identify the label A in the above diagram.
(a) Chromatin fibre
(b) nuclear pore
(c) Kinetochore
(d) None of these
(ii) Choose the correct pair.
(a) Histones — Basic proteins
(b) Centromere — Secondary constriction
(c) Kinetochore — Kidney-shaped structure
(d) None of the above
(iii) For the study of structure of nucleus, the best cell is
(a) cell in the interphase
(b) cell in the late prophase
(c) cell in the divisional phase
(d) cell in the meiotic phase
(iv) Which of the following table refers correctly to the chromosome?

(v) Which of the following stains is not used for staining chromosomes?
(a) Basic fuschsin
(b) Safranin
(c) Methylene blue
(d) Carmine
- Answer Key-
- Multiple Choice Answers:
- (d) Palade.
- (d) F0-F1 complex (Oxysome)
- (d) Vacuole.
- (c) Intussusception.
- (c) A porous double membrane.
- (a) Interconnected sacs.
- (c) Mitochondria.
- (b) Cell wall
- (d) Chitin
- (d) Cell adherence.
- (b) Some proteins embedded and some on the surface.
- (c) Robertson.
- (d) Protein synthesis.
- (b) Nucleolus.
- (a) Chloroplast.
- Fill In the Blanks:
- cells, unicellular, multicellular
- cell biology
- Robert Hooke
- Robert Brown
- Schleiden, Schwann
- division of labour
- True or False:
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- Very Short Answers:
- Answer: Waldayer.
- Answer: A clear layer of oligosaccharide outside the cell membrane in some animal cells.
- Answer: In microtubules of flagella.
- Answer: It is defined as the ER found in striated muscles.
- Answer: Pili are elongated, tubular structure in Gram-ve bacteria.
- Answer: Fimbriae are small, bristle-like fibers sprouting out of the cell in bacteria.
- Answer: Lysosomes are called suicidal bags of the cell.
- Answer: The cytoplasm is a jelly fluid of protoplasm composed of inorganic and organic matters containing many organelles like ribosomes, ER, vacuole, etc.
- Answer: Plasmodesmata are connections between two cell walls that are interrupted by small pores having fine threads of cytoplasm.
- Answer:
1. filament
2. hook and
3. basal body.
- Short Answer:
- Answer: Fundamental similarities in all cells are:
1. Hereditary characters are transmitted through nucleic acids.
2. The basic structure of membranes of all cell organelles is the same.
3. Method of aerobic respiration.
4. Mechanism of synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins within the cells.
- Answer: Cytoskeletal Structures: The ability of eukaryotic cells to adopt different types of shapes and to perform directed movement depends on the cytoskeleton.
There are three principal types of protein filaments
1. Microfilaments,
2. Microtubules, and
3. Intermediate filaments.
These constitute the cytoskeleton. The microfilaments are 8 nm in diameter, either scattered or organized into the network or parallel arrays within the matrix. They play a major role in cell motion (changes in shape). Such cellular movements associated with the microfibres are movements of pigment granules, amoeboid movements, and protoplasmic streaming. These microfilaments consist of actin-like proteins.
- Answer: The main functions of the cell wall are:
1. It gives a definite shape to the cell and protects the internal organelles.
2. It provides a framework and lends support to the plasma membrane.
3. It prevents the cell from desiccation.
4. It counteracts physically the osmotic pressure produced by the cell contents.
5. It helps in the transport of materials and metabolites in and out of the cell.
- Answer: The functions of Golgi bodies are:
- Storage, condensation, and packaging of the material.
- Several enzymes are localized in Golgi bodies.
- During spermatogenesis, Golgi apparatus form the euro some.
- Mucilage and gums are secreted in plant cells due to the action of the Golgi apparatus.
- Answer: There are two types of EM.
i. Smooth ER (Agranular) and
ii. Rough ER.
- Answer: With the increase in size, volume increases but surface area exposed to the environment does not increase correspondingly. This limits the exchange of information and materials through the surface. As a result efficiency of the cell as an autonomous unit decreases.
- Answer: The cell is an open system because it allows the entry and exit of matter and energy. It takes up food, oxygen, water, and salts for its substance, growth, and division. The cell also takes up energy from- food and operates the metabolic processes. It gives out waste products, secretions, and energy.
- Answer: The cell can be considered as an autonomous unit because:
1. Each cell-carries out all fundamental biological processes independently.
2. Each cell oxidizes food material and utilizes that energy and some nutrient molecules to synthesize complex molecules.
3. The cell uses these molecules to build new structures and to replace worn-out cells.
4. The cell respires and exchanges gases with the environment.
5. It reproduces to form new cells with similar hereditary characters,
6. It also maintains an internal physiochemical environment.
- Long Answer:
- Answer: Every cell is enclosed on all sides by the distinct covering called the plasma membrane.
1. It maintains the individuality of the cell by preventing the mixing of cell contents with extracellular materials.
2. The cell is not a sealed compartment and the exchange of materials is allowed by the cell membrane in a selective and regulated manner.
3. In animals, the cell membrane has on its surface certain chemical that can recognize cells of the same kind. This helps the cells to aggregate and defend themselves against microbes.
4. The cell membrane also receives messages from outside and passes them to adjacent cells.
5. The cell membrane selectively allows the passage of certain molecules and ions from the seawater to enter the cells of organisms living in the sea.
- Answer:
- It is true that the cells of unicellular organisms tend to be spherical. It is because of the following reasons.
- Surface tension: Surface tension shapes the spherical way as in the case in air-borne soap bubbles.
- The free-floating cells with thin membranes tend to be spherical as it is the most economical shape that can confine a given mass of protoplasm.
However, the shape and the size of the cell depend upon the place where they are present and the functions they have to perform. In multicellular animals, the cells tend to become faceted as they come in contact with each other in the same way as the spherical soap bubbles become flattened when they are jammed together in a small space.
This phenomenon can be best seen in the early stages of the development of an embryo. The cell mass still remains spherical for some time but when the cells multiply the shape changes because of adjusting themselves to the available space. This is also true in plants, they have in addition cellulose also.
But the most important aspect of cell shape is the functions each cell has to perform.
- Answer: Methods of science and cell theory: Scientific method of solving a problem is a realistic approach and it helps us in finding out the truth.
The scientist after making observations of many samples proposes a hypothesis that is subject to be tested before it is taken as a theory.
i. In the case of cell theory Theodor Schwann after examining many types of tissues found that all these have cells and the cells have a nucleus and cytoplasm universally present and then after comparing its structure to that of plant cells proposed a hypothesis that bodies of animals and plants are composed of cells and products of cells.
ii. This hypothesis was later confirmed by Schleiden who examined a large variety of plant tissues and found all of them to be composed of cells. Thus the hypothesis of Schwann become a theory of Schleiden and Schwann.
Further, as the scientific method says a theory can be changed, modified, or discarded on the basis of new discoveries. The cells theory of Schleiden and Schwann was modified by Rudolf Virchow who was the first to explain that, “cells divide and all-new cells must come from pre-existing cells.”
Thus we can say that method of science is fully reflected in the formulation. of the cell theory.
- Answer:
1. To maintain the organization of living organisms every system of energy, try to reduce entropy. Entropy is the degree of randomness. If the system is left on its own it increases in entropy.
2. Earth receives a continuous supply of energy from the sun in the form of photons of light.
3. 0.2 to 1% of the solar energy received by the earth enters the biosphere in the form of chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. Heterotrophs depend upon autotrophs for food.
4. Flows of energy take place from photosynthesizers to heterotrophs „
forming food chains and food webs.
5. Approximately 10% of the energy is conserved at each trophic level. This is how earth maintains so many living organisms in a highly organized state.
- Answer: Structure of Mitochondria: They are spherical or elongated or rod-like cell organelle. Mitochondria were first discovered by Hofmeister in the cells of a pteridophyte, Equisetum. They were named ‘Mitochondrion’ by Benda.
Mitochondria is a double membranous organelle, the outer membrane is smooth while the inner one is folded into a number of cristae. The space between the two membranes is called the outer chamber while the space surrounded by the inner membrane is an inner chamber that is filled with homogenous fluid. The inner membrane has a large number of F, particles or exosomes.
These are the sites for oxidative phosphorylation. Each Oxysome has a head, stalk, base; The number of elementary particles in a mitochondrion maybe 104-105. The head of F, particle contain ATP synthetase enzyme hence they are said to be ATP particles.

Mitochondria from animal cell
Functions of mitochondria:
1. A powerhouse of the cell and store energy as ATP.
2. Several respiratory enzymes are found in mitochondria.
3. DNA is also contained in mitochondria.
4. They regulate the concentration of calcium ions in the cells.
Assertion Reason Answer-
- (a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Explanation: Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of organism.
- (a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Explanation: Specialization of the cell increases the efficiency of the cell for a particular function.
Case Study Answer-
- Answer:
(i) (b)
(ii) (c)
(iii) (a)
(iv) (d)
(v) (b)
- Answer:
(i) (c)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (a)
(iv) (b)
(v) (b)
Class 11 Biology All Chapter Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 The Living World Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation In Animals Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell The Unit Of Life Notes and Question Answer
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Notes and Question Answer

